Landsat’s Role in Managing Water Resources
Water is essential for life. A third of Earth’s populace has unreliable access to clean water. With current population growth and environmental trends, the U.N. Environmental Program estimates that 1.8 billion people will face water scarcity by 2025. Water means survival for people and other species we rely upon to thrive, making proper stewardship of our water resources vital. Good decisions require good data. Since 1972 the Landsat series of satellites has been providing such data. Landsat-based decisions on how to manage limited water resources have impacted millions of people worldwide. From finding water for refugees in arid nations to reducing pollution in our national waterways, Landsat enables decisions that directly help people.
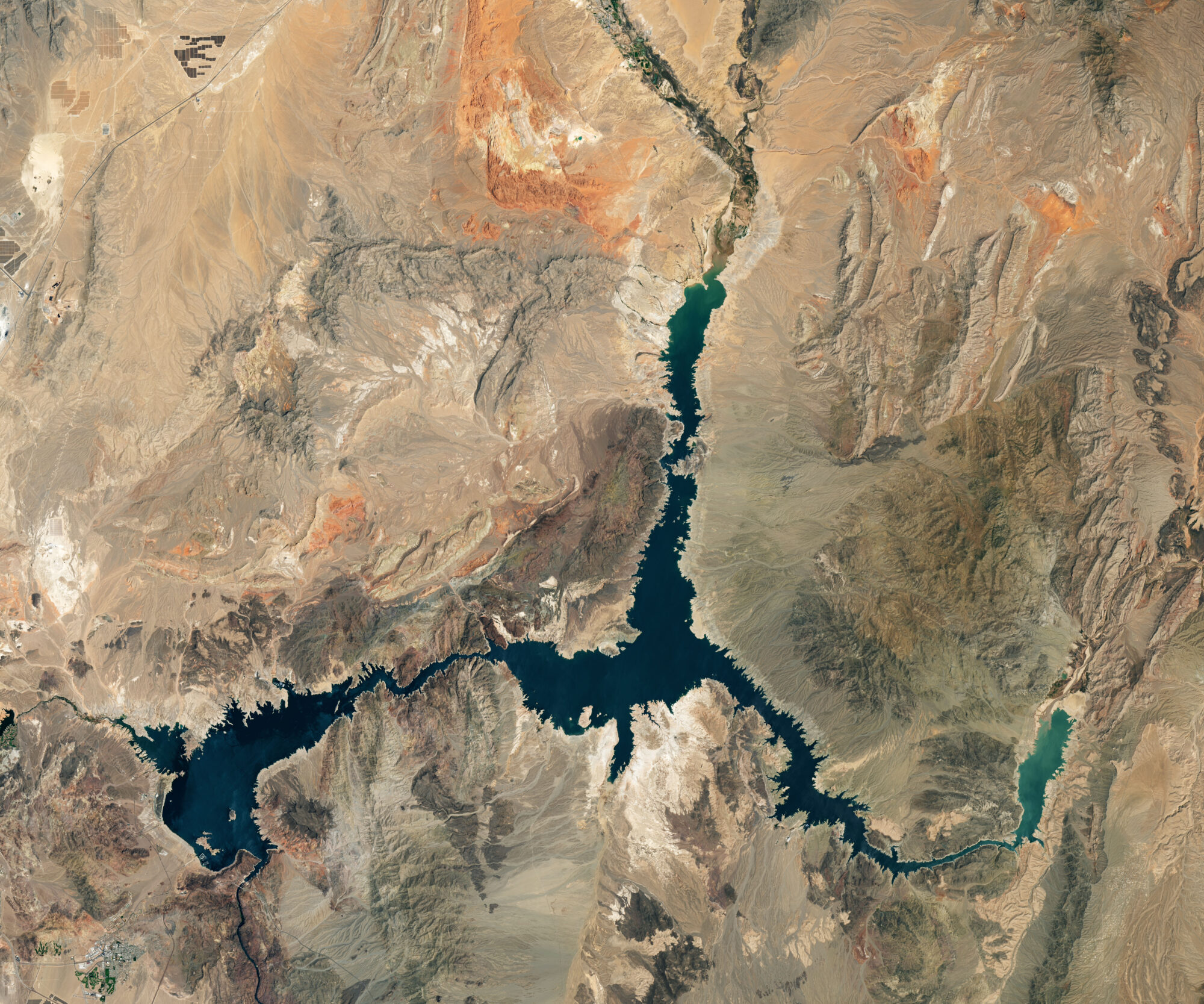

Mapping Reservoirs for Better Water Management
Using data from Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 (HLS), researchers developed a new algorithm to better monitor reservoir water levels in the contiguous U.S.

Celebrating 53 Years Since Landsat 1’s Launch
When the first Landsat satellite launched in 1972, it posed the following question: could we manage our natural resources using remotely–sensed data? The answer, 53 years on, is a resounding “yes.”

Shifting Coastlines in the Arctic
The Arctic is changing rapidly. Recent research unveiled a new dataset of 40 years of coastlines shifting across the Arctic.
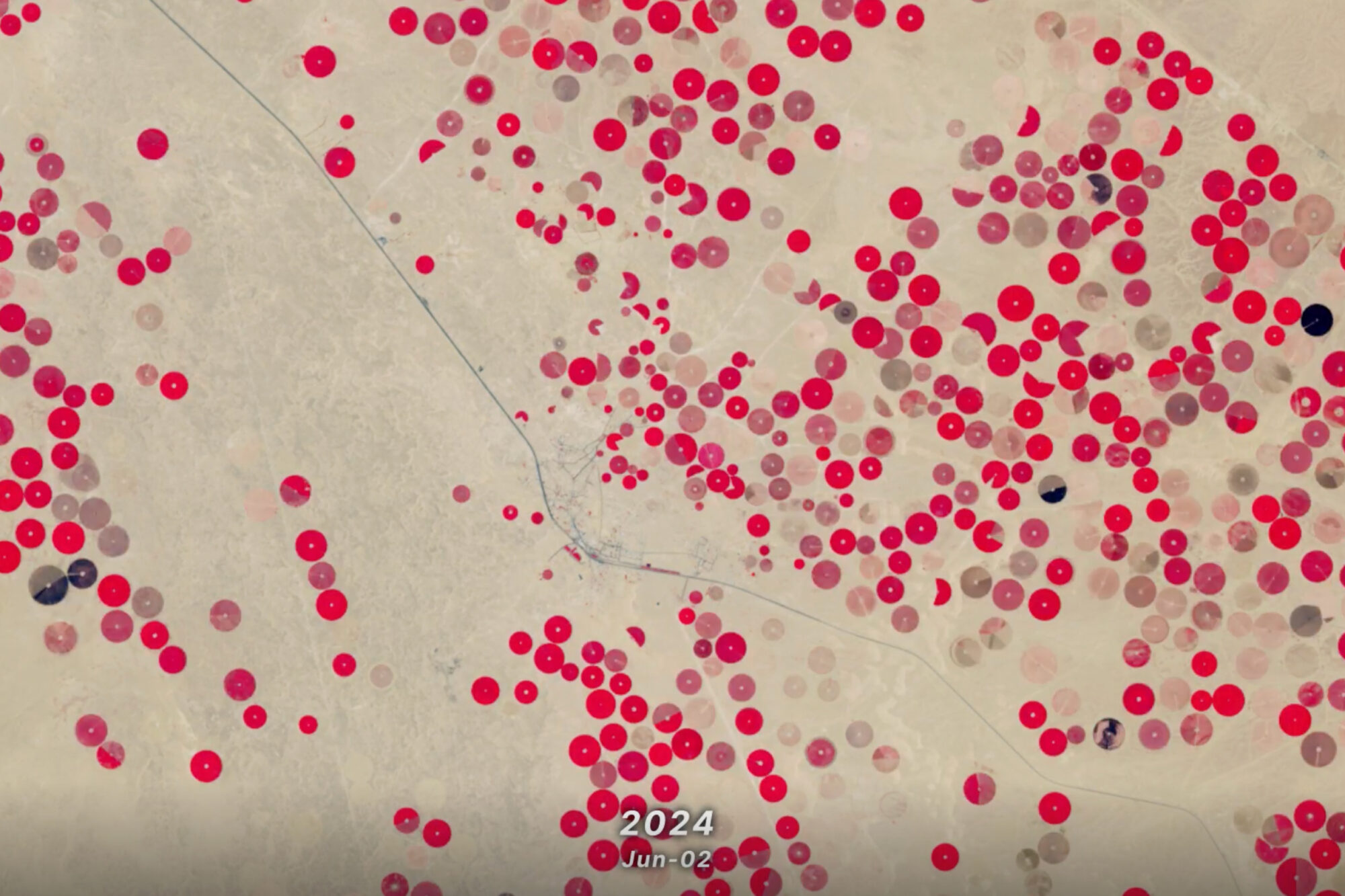

Saudi Arabia’s Desert Agriculture
In this animation of 2024 and January 2025, crop fields in Saudi Arabia cycle through their growing seasons.

Landsat at Work: Conserving Water and Growing High Quality Grapes
Using Landsat’s thermal imagery, researchers at Gallo Winery have been able to better understand vineyard water needs and optimize irrigation.
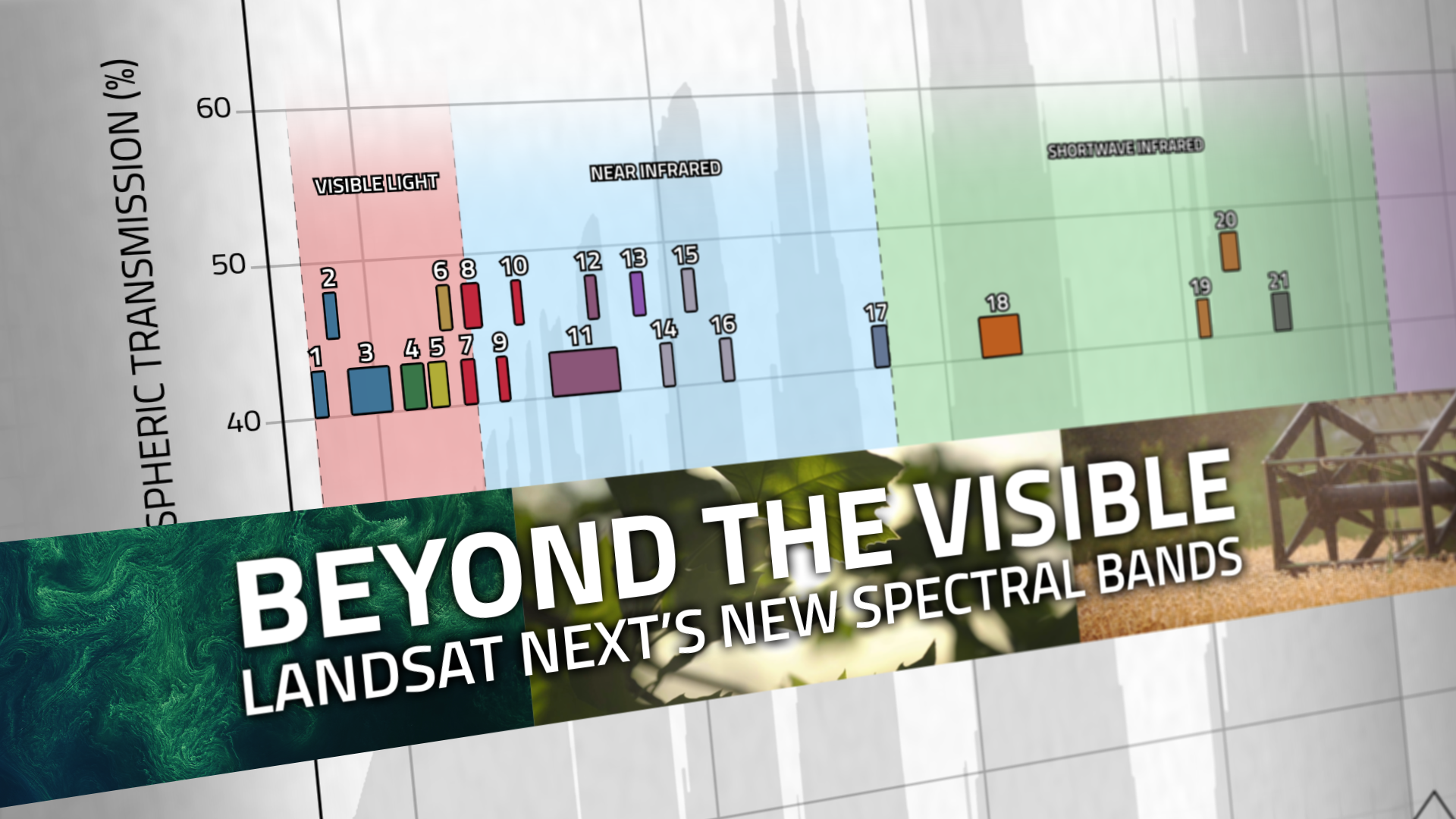
Beyond the Visible: Landsat Next’s New Spectral Bands
With Landsat Next’s 26 new spectral bands, we’ll be able to see our planet like never before. Landsat Next’s enhanced capabilities will provide scientists, farmers, and decision-makers with critical data to tackle global challenges.

