Landsat’s Role in Managing Water Resources
Water is essential for life. A third of Earth’s populace has unreliable access to clean water. With current population growth and environmental trends, the U.N. Environmental Program estimates that 1.8 billion people will face water scarcity by 2025. Water means survival for people and other species we rely upon to thrive, making proper stewardship of our water resources vital. Good decisions require good data. Since 1972 the Landsat series of satellites has been providing such data. Landsat-based decisions on how to manage limited water resources have impacted millions of people worldwide. From finding water for refugees in arid nations to reducing pollution in our national waterways, Landsat enables decisions that directly help people.
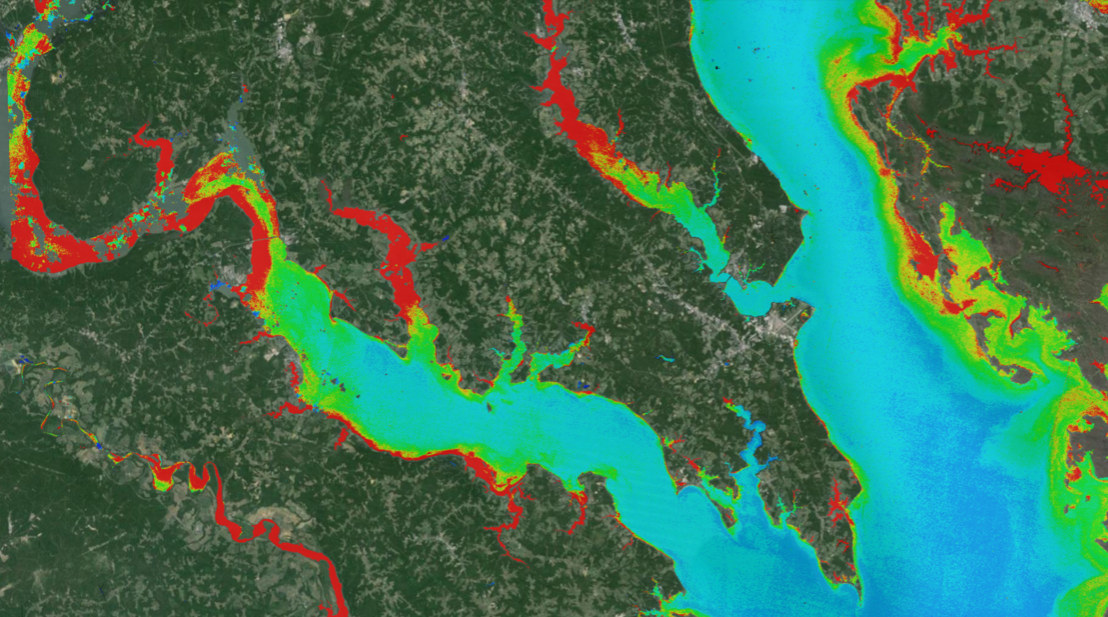
New Tool Provides Rapid Evaluation of Water Quality
A combination of Landsat and Sentinel-2 imagery, NASA near real-time data, and machine learning provides near real-time access to high-resolution water quality maps.
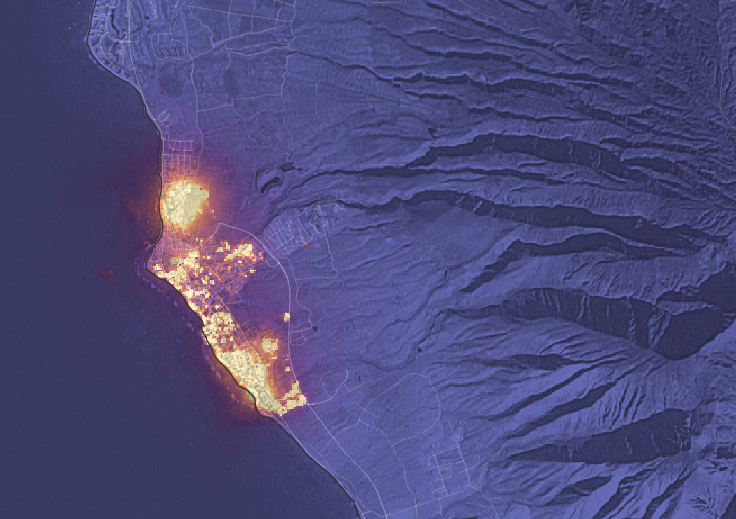
Landsat Observations Key Resource for Many Federal Agencies
In the FY23 Aeronautics and Space Report released on May 23, 2024, a multitude of Federal agencies report work informed by Landsat data.

Meat of the Matter: Colorado River Over-Consumed
More water is taken from the Colorado River than it has to give. Better water use accounting made possible by Landsat provides needed guidance for difficult water use decisions.
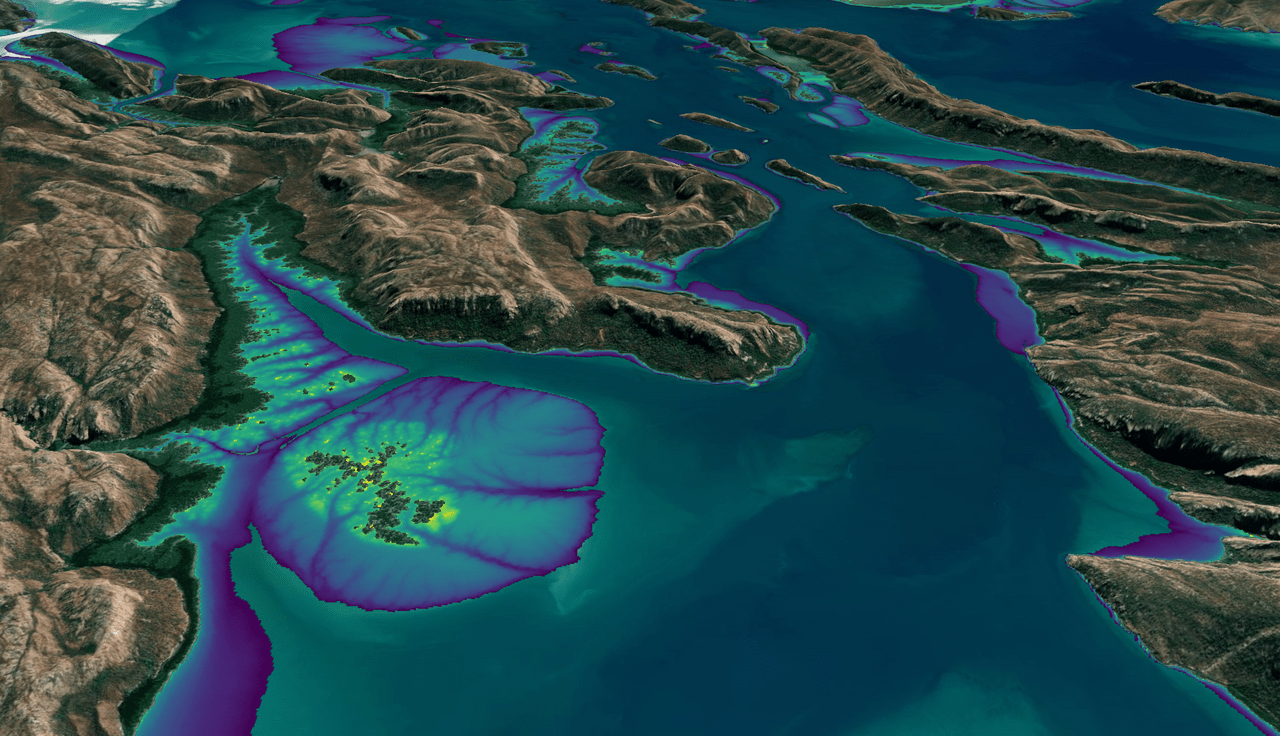
Australian Intertidal Zone Exposed: Landsat and Sentinel-2 Provide Information on Dynamic Region
This month, the Digital Earth Australia (DEA) team released a new Landsat and Sentinel-2 based intertidal data product. The new data set characterizes the tidal shoreline zone of Australia in more detail than ever before.

Data in Harmony: NASA’s Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 Project
NASA’s Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 (HLS) project is a groundbreaking initiative that combines data from Landsats 8 & 9 with the European Space Agency’s Sentinel-2A & 2B satellites.
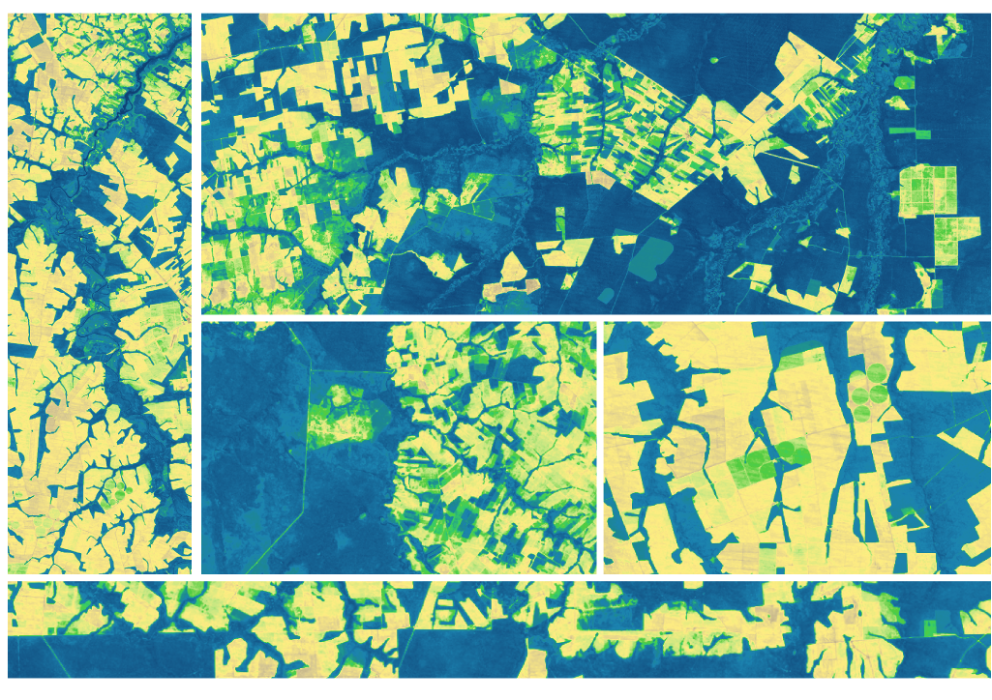
Expanding OpenET Across Amazon Basin
The research teams who help sustain the largest freshwater reserve in the world are developing a new tool to promote more resilient farming systems in Brazil. The goal is to help farmers better handle changes in the water cycle, deal with droughts, and adapt to a changing climate.


