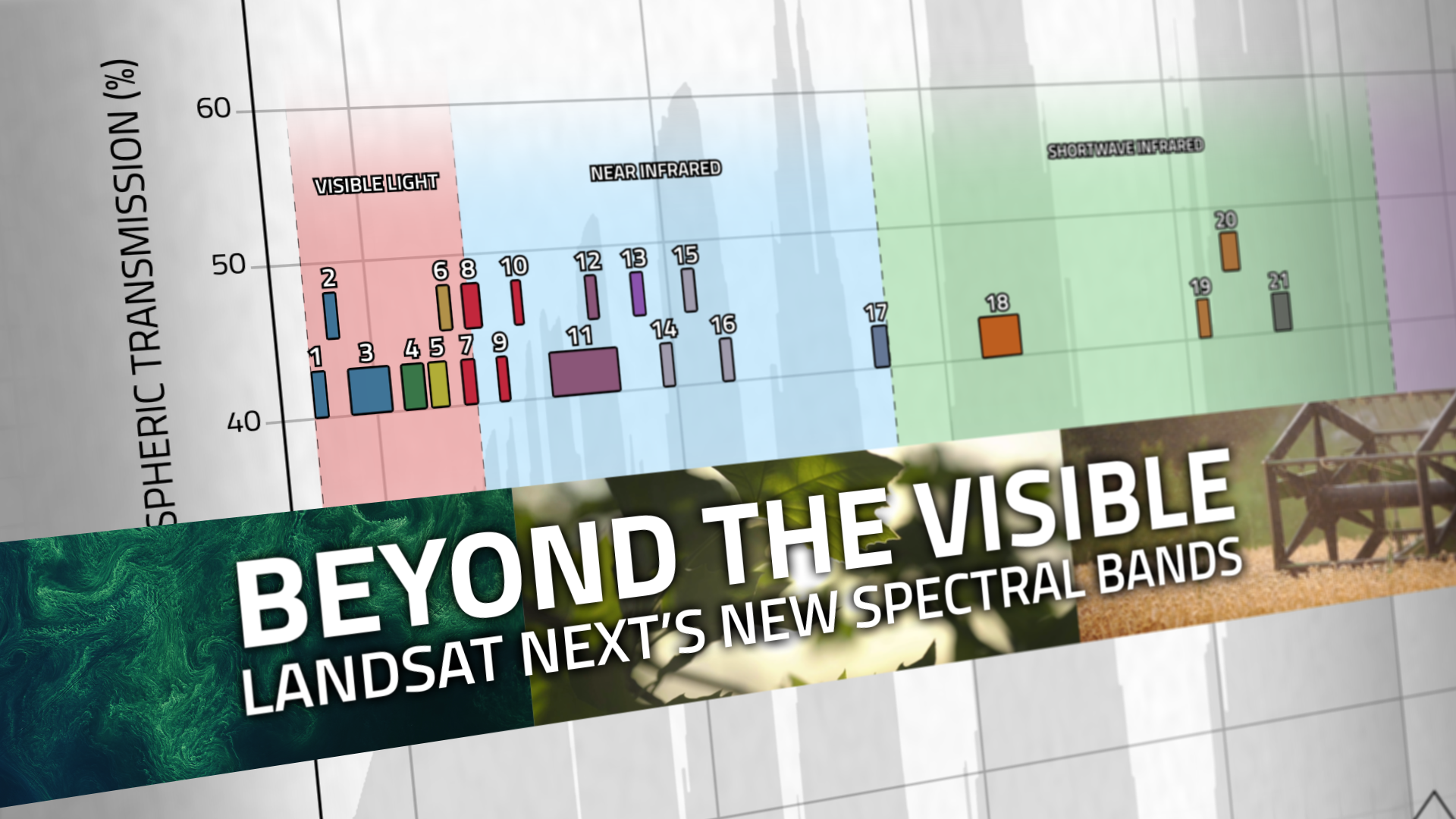
Beyond the Visible: Landsat Next’s New Spectral Bands
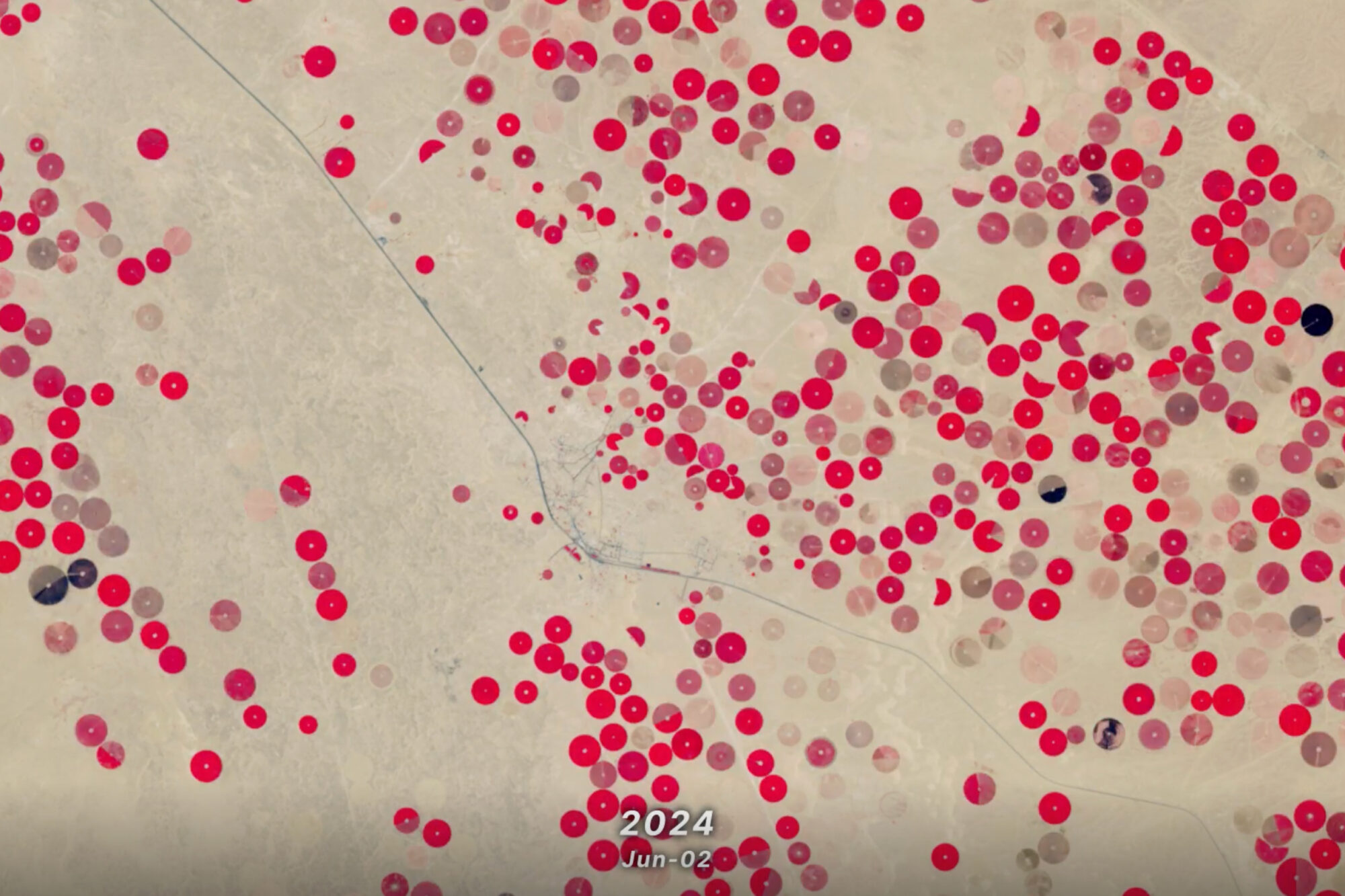
With Landsat Next’s 26 new spectral bands, we’ll be able to see our planet like never before. Landsat Next’s enhanced capabilities will provide scientists, farmers, and decision-makers with critical data to tackle global challenges.