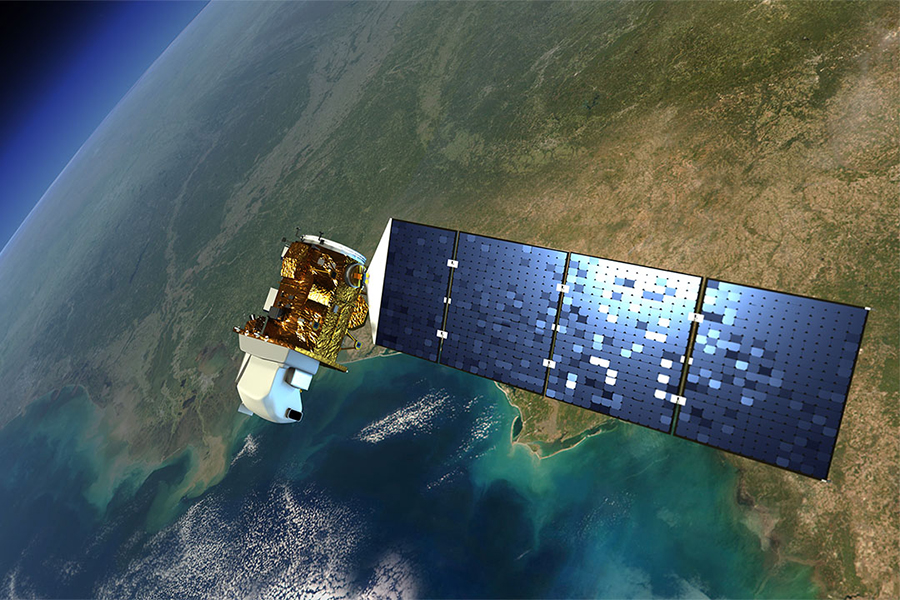
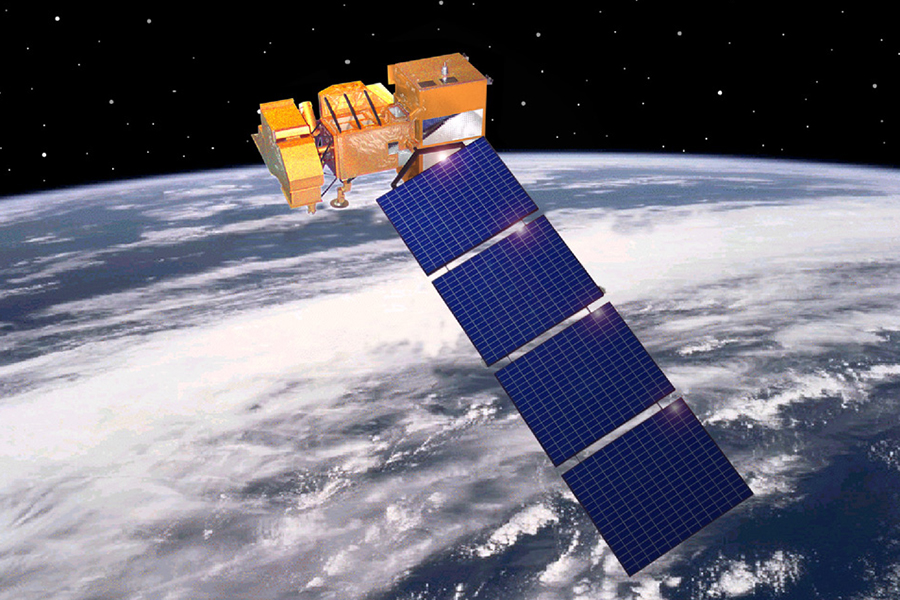
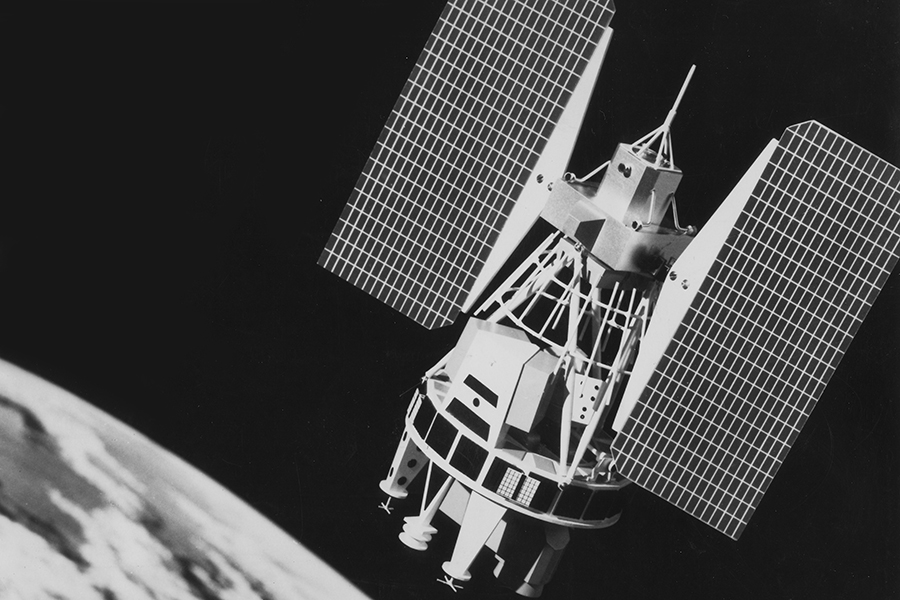
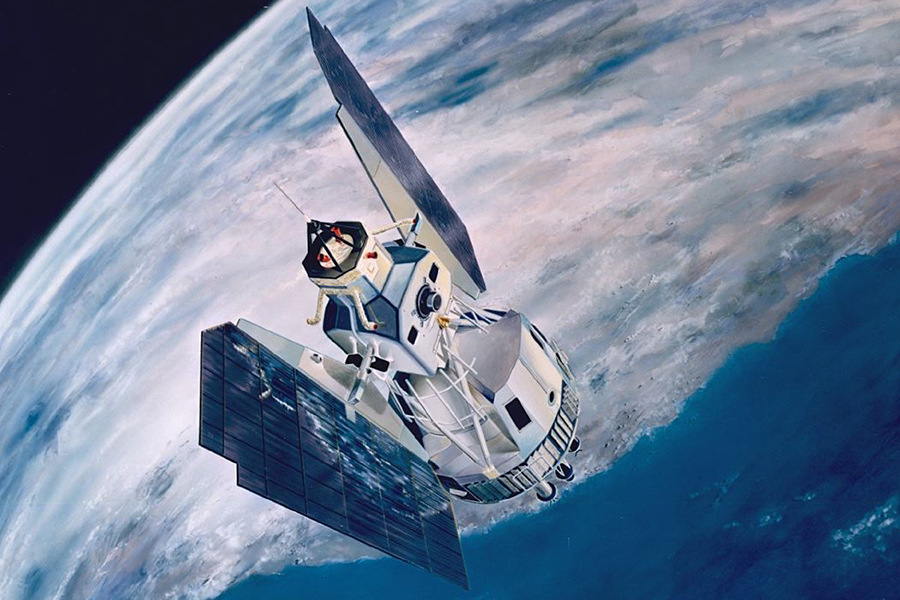
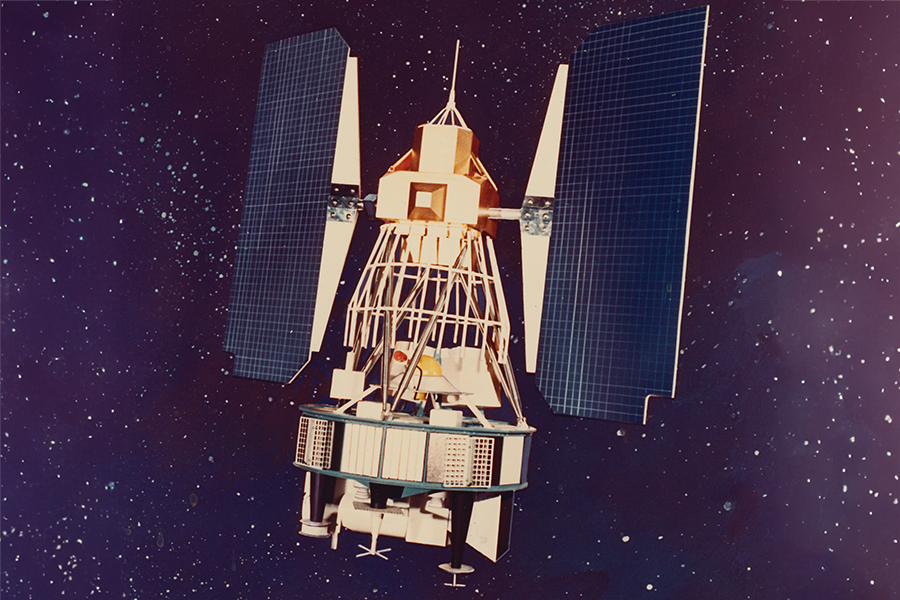
The Landsat program consists of a series of Earth-observing satellite missions jointly managed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). To date, there have been nine missions, eight of which have been operational. The tenth mission, Landsat Next, is in its preliminary phases and is planned to launch in late 2030. Since the launch of Landsat 1 (formerly known as ERTS-1) in 1972, Landsat satellites have continuously and consistently captured images of the Earth’s land surfaces. With over five decades of observations, the Landsat program has created a data archive of unmatched quality and coverage that has vastly improved our understanding of the Earth, its natural resources, and its dynamic processes.
The Landsat program was conceived in 1966 largely as a direct result of the demonstrated utility of the Mercury and Gemini orbital photography to Earth resource studies. Over the course of mission operations, there has been an intriguing, rich, and unpredictable history that was shaped by key agencies and prominent individuals.