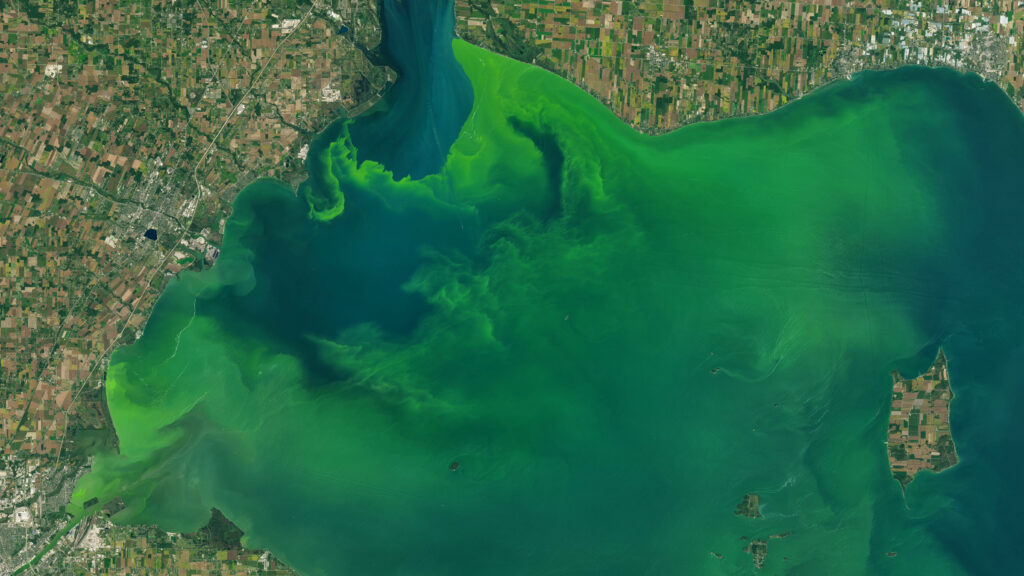
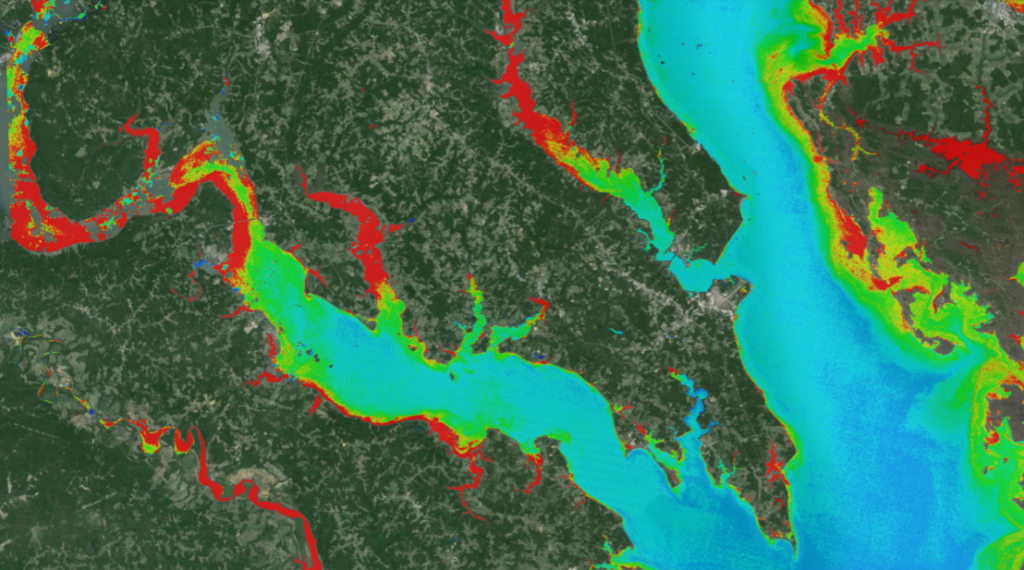
Space News has reported that the European Space Agency (ESA) is planning to offer data from its Global Monitoring for Environment and Security (GMES) project for no cost. The article sites the success of the Landsat free data policy as an impetus for this move.
Excerpted from Space News [external link]:
Access to U.S. Landsat data used to be subject to fees. Since it has been available free of charge, downloads of Landsat data has increased “exponentially,” said Timothy Stryker, director of policy, plans and analysis for land remote sensing at the U.S. Geological Survey.
The August 2008 decision to make the archives of Landsat data available on the web without charge has resulted in a 60-fold increase in the number of scenes downloaded per day, with U.S. and Chinese users being the most frequent of the 186 nations that have taken advantage of the service, Stryker said here June 28.
“In our best year of sales, 2001, we distributed an average of 53 scenes per day,” Stryker said. “The average has been increasing steadily and is around 3,125 scenes per day of web-enabled data. We passed the million-scene mark in August 2009 and passed 2 million scenes on March 13.”
In addition to the sheer numbers, Stryker said more users are now asking for multiyear images of the same area for land-use and environmental-change studies.”