Landsat’s Role in Managing Forests
People and economies around the world rely on forests for timber, carbon storage, flood control, biological diversity, recreation, and more. Forest managers face many challenges. In the last few years, forest fires have become more intense and more frequent; North American forests have experienced widespread infestations by pests such as the pine bark beetle; and tropical deforestation continues. Our changing climate adds complexity to government and commercial decisions about how to manage, protect, and sustain our forest resources. Landsat satellites provide key data for forest monitoring and management across the globe. Landsat gives us consistent views of the health, composition, and extent of forest ecosystems as they change over time. Curtis Woodcock, Professor, Boston University and specialist in remote sensing, has said, “I would argue that the Landsat data archive may be the most valuable environmental data record we have.” Designed, built, and launched by NASA, Landsat satellites have recorded global forest conditions every year since the 1970’s, and they have observed all U.S. forests once a season throughout those years. The U.S. Geological Survey provides this valuable data to the public at no cost. Landsat observations will continue into the future with Landsat 8.
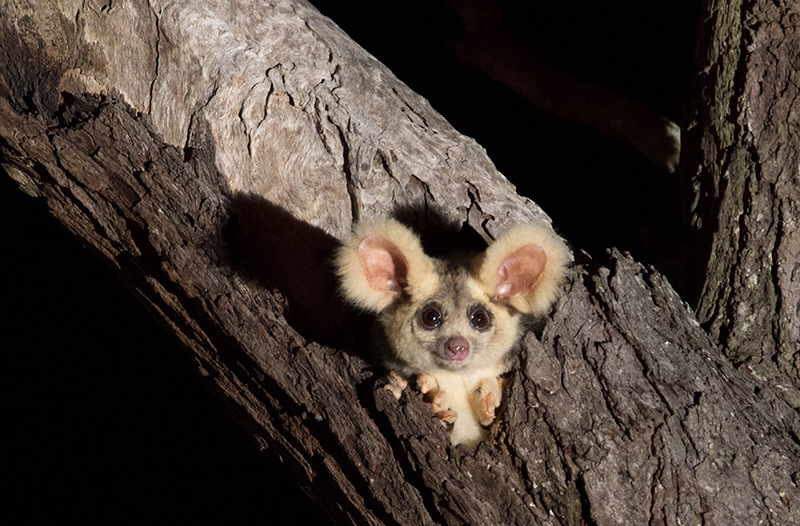

Landsat Helps Prioritize Conservation Areas for Australia’s Gliding Possums
Using satellite data, including Landsat, Griffith University researchers found that less than 13 percent of the endangered greater gliders’ habitat in Queensland is protected.

ExtraDimensional—The Fusion of Landsat & GEDI
When Landsat’s vast decades-long archive is combined with data from other instruments it can provide amazing insight into how our world is evolving with us and around us. Here are some of the ways Landsat and GEDI data are being harnessed to help us better understand the complex relationship between humanity and nature.

Joining Jane Goodall in Conserving Chimpanzee Habitats
The Jane Goodall Institute has been working with NASA and using Earth science satellite imagery and data—including Landsat (NASA/USGS)—in its chimpanzee and forest conservation efforts in Africa, particularly the Gombe region.

From Orbit to A.I.—Harnessing Machine Learning with Landsat Data
Over the past few years, machine learning techniques have been increasingly used to analyze the vast amount of data collected by the Landsat mission, which has been circling the globe for over 50 years.
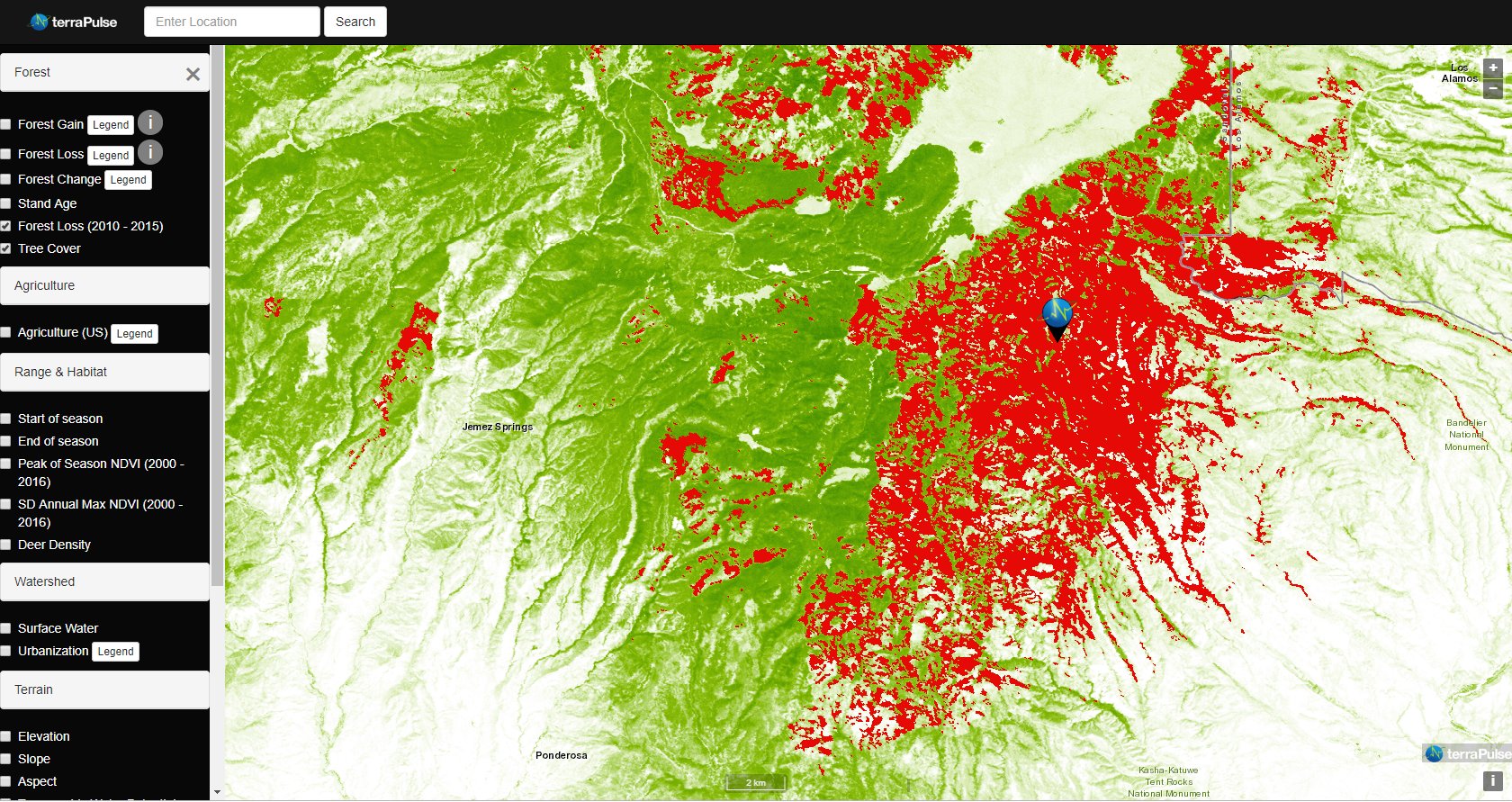
Taking the Pulse of Earth
Applying AI to Earth data—including Landsat—helps terraPulse reveal sustainable options for farming, reforestation, and land management.

NASA-Led Project Tracking Changes to Water, Ecosystems, Land Surface
Merging data from multiple satellites, OPERA can help government agencies, disaster responders, and the public access data about natural and human impacts to the land.

