by Kathryn Hansen, NASA Earth Observatory
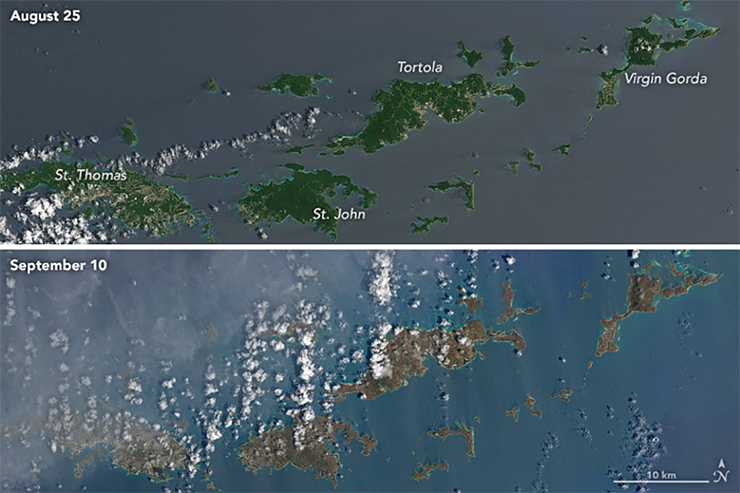
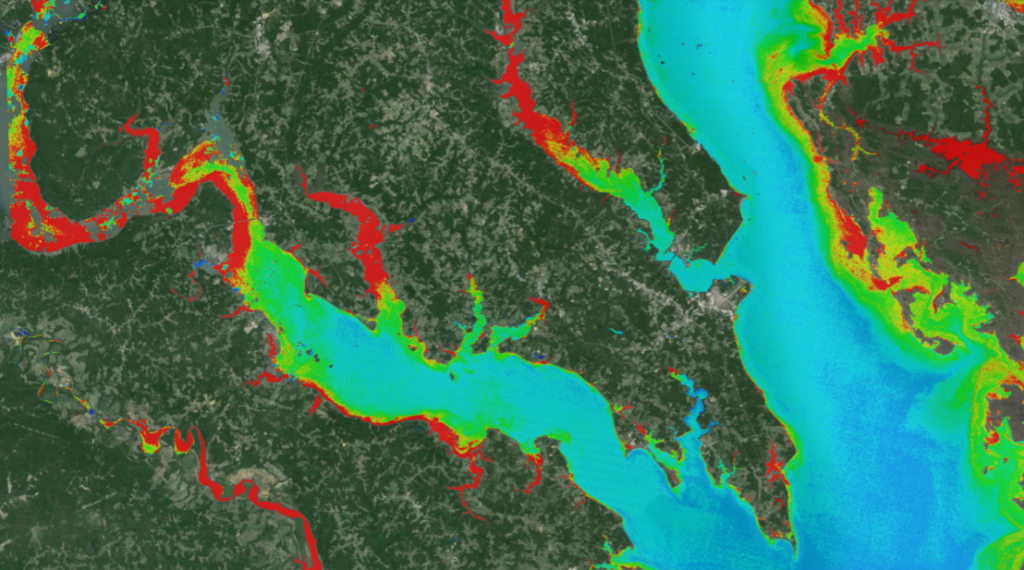
These natural-color images, captured by the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on the Landsat 8 satellite, show some of Irma’s effect on the British and U.S. Virgin Islands. The views were acquired on August 25 and September 10, 2017, before and after the storm passed. They are among the few relatively cloud-free satellite images of the area so far.
The most obvious change is the widespread browning of the landscape. There are a number of possible reasons for this. Lush green tropical vegetation can be ripped away by a storm’s strong winds, leaving the satellite with a view of more bare ground. Also, salt spray whipped up by the hurricane can coat and desiccate leaves while they are still on the trees.
Irma passed the northernmost Virgin Islands on the afternoon of September 6. At the time, Irma was a category 5 storm with maximum sustained winds of 185 miles (295 kilometers) per hour. According to news reports, the islands saw “significant devastation.”

Be Part of What’s Next: Emerging Applications of Landsat at AGU24
Anyone making innovative use of Landsat data to meet societal needs today and during coming decades is encouraged to submit and abstract for the upcoming “Emerging Science Applications of Landsat” session at AGU24.