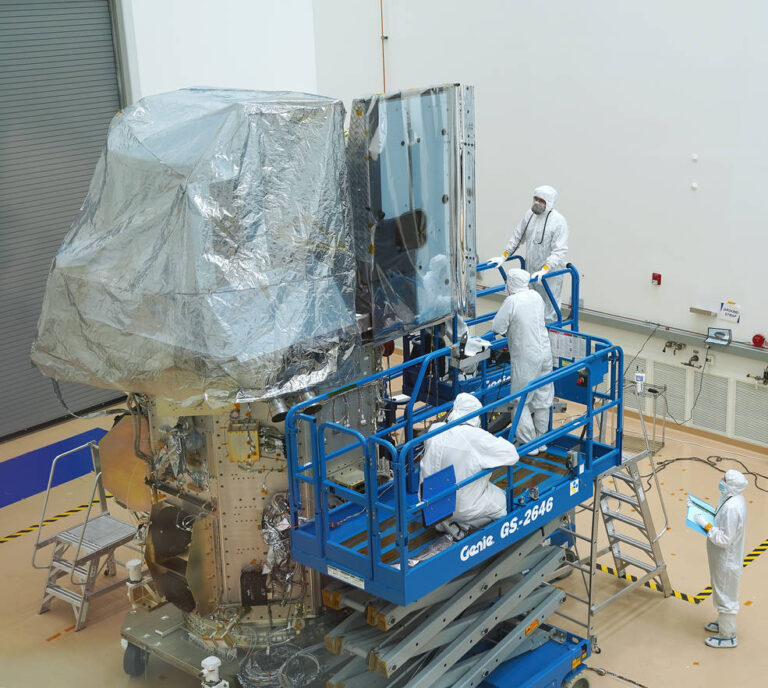
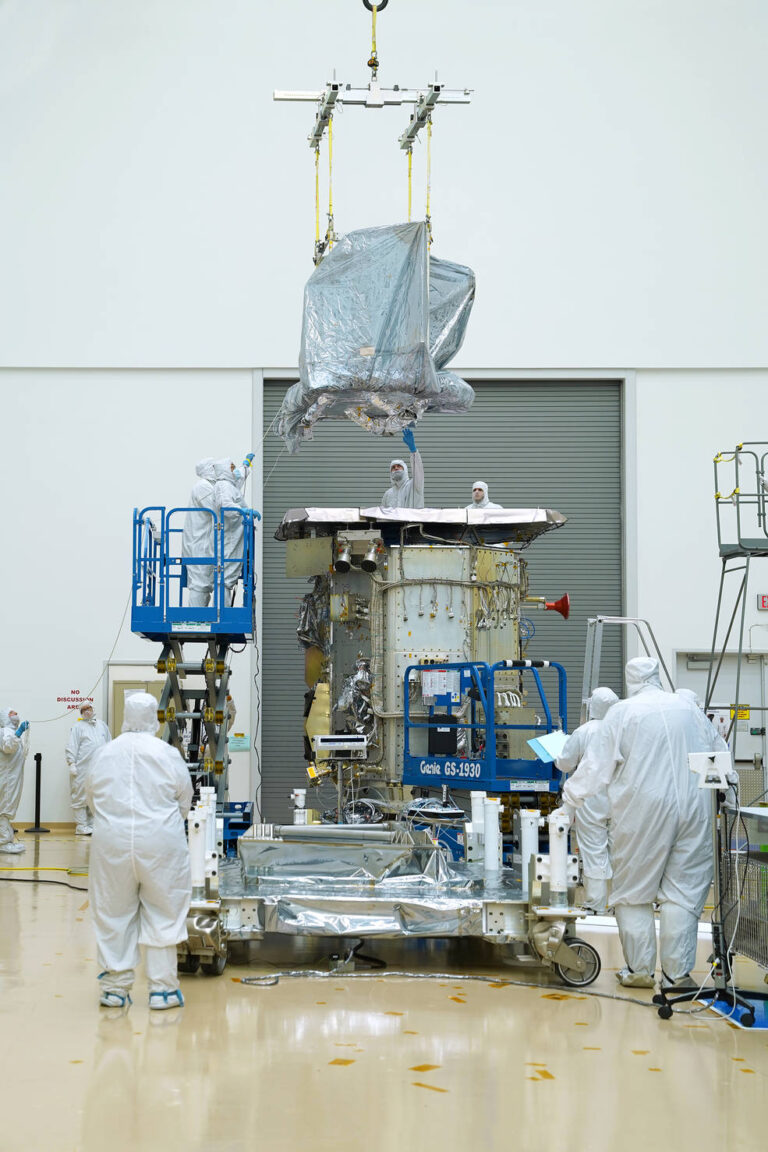
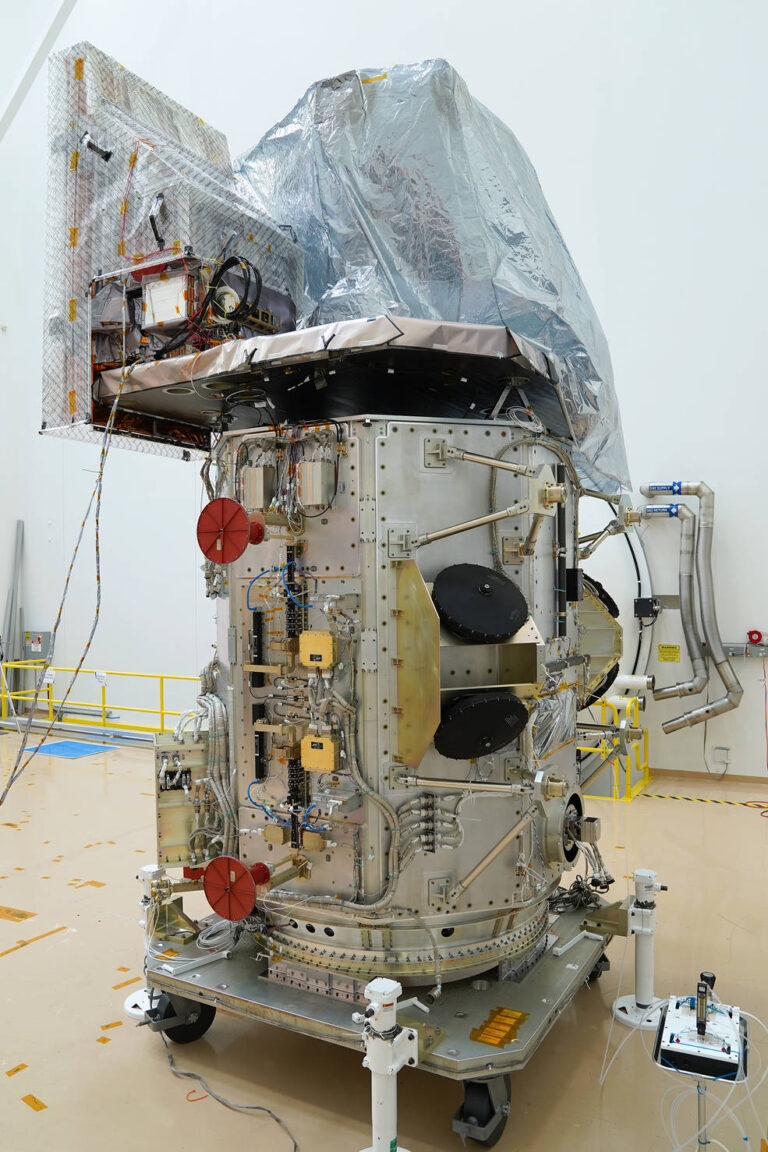
Landsat 9’s two science instruments are now attached to the spacecraft, bringing the mission one step closer to launch. In late December, the Operational Land Imager 2 (OLI-2) and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) were both mechanically integrated on to the spacecraft bus at Northrop Grumman in Gilbert, Arizona.

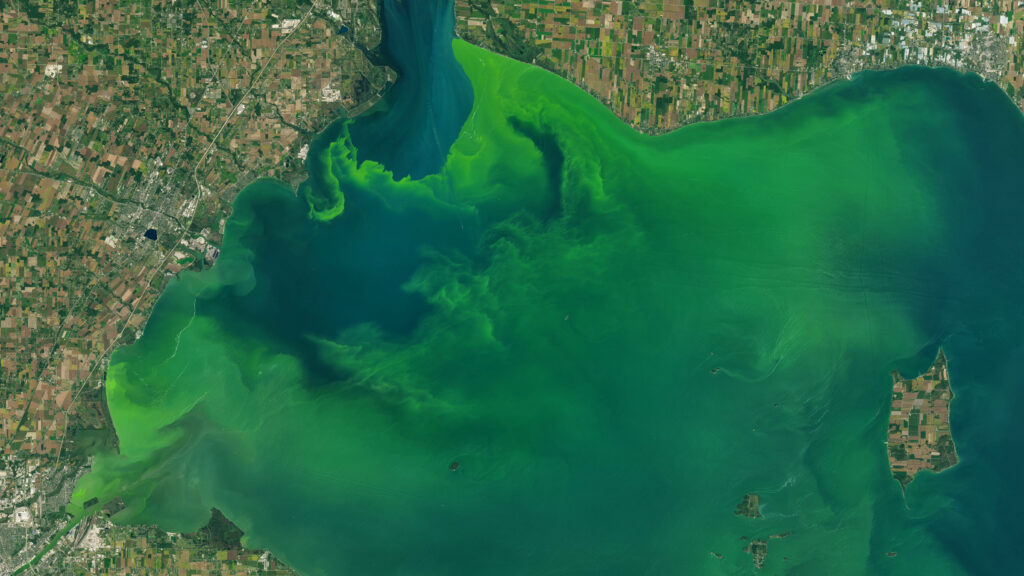
The Landsat 9 mission continues the nearly 50-year Landsat data record, providing actionable information to resource managers and policymakers around the world. Landsat 9 will record the condition of Earth’s ever-changing land surface, enabling scientists and others to monitor crops and algal blooms, to assess deforestation trends and urban growth, and to aid disaster management.

Landsat is a collaboration between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. NASA oversees the design, build, and launch; USGS operates the satellites on orbit, and manages the expanding data archive.
Engineers will next work on the electrical integration of the instruments, which includes getting power to the instruments and incorporating the satellite’s data-handling hardware.
The OLI-2 instrument makes measurements of Earth’s reflectance in the visible, near infrared, and shortwave infrared; the TIRS-2 instrument extends measurements made by Landsat 9 into the thermal infrared, providing information about the surface temperature. Water managers across the American West, as well as arid regions across the globe, rely on the highly calibrated measurements made by Landsat 8’s Thermal Infrared Sensor to monitor irrigation and water usage and they are eager to have the record continued by Landsat 9’s TIRS-2. Reflected light measurements by the OLI-2 instrument are in turn used to map global land cover, ecosystem health, water quality, glacier flow, and other critical Earth surface properties.

Related Reading:
+ Landsat 9 Instrument Ready for Spacecraft Assembly
+ New Landsat Infrared Instrument Ships from NASA
By: Laura E.P. Rocchio, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center