Landsat’s Role in Supporting Urban Planning
Cities are places of light, action, complex social interactions, multi-faceted cultures, and fast-paced living. It’s no wonder cities are growing faster than rural areas. Earth experienced a milestone in the history of urban landscapes in 2008-09. More than 50 percent of the world’s human population now lives in areas of contiguous urban development. People are driving landscape-scale changes on our planet. Considering that people change the land surface, vegetation, water cycle, radiant heat, and other aspects of the landscape, the nature of this milestone has important implications for life. Using Landsat data, people can monitor urban change and also forecast patterns of change in future urban landscapes. Landsat sensors employ a spatial resolution of 30 m, an ideal scale for observing human impacts on the land. The sensors detect urban growth with visible and infrared reflectivity consistently, objectively, and dependably over time.
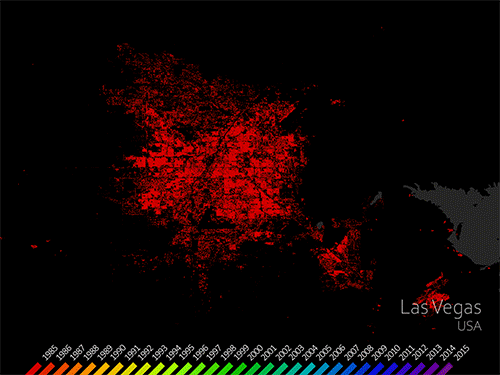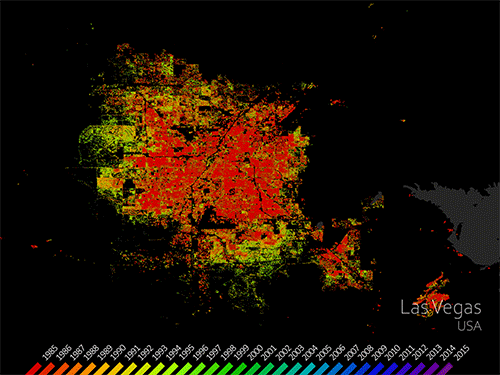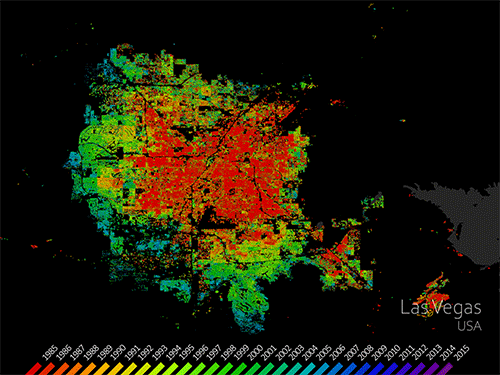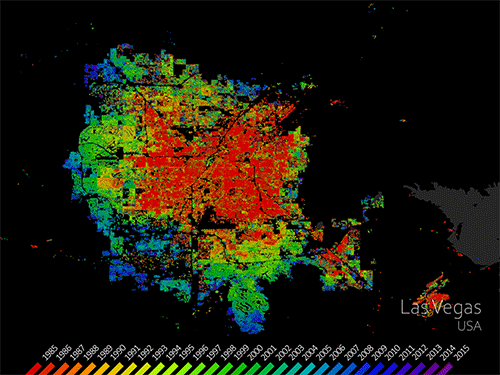
Mapping Our Human Footprint from Space
The World Settlement Footprint is the world’s most comprehensive dataset on human settlement.

Landsat Helps Urban Planners Find Disparities in Access to Green Spaces
Study of two metro areas finds where parks, trees and other green spaces are located.

Understanding the Ecological and Environmental Impacts of Urbanization
Landsat-based urban extent and phenology indicators provide new information about urban environments.

How Urban Heat Affects the Socially Vulnerable in Sun Belt Cities
Socio-economically vulnerable populations are at a higher risk of experiencing urban heat effects.

Hot in the City, And Hotter Still in Low-Income Areas
A new investigative report published by NPR has found that it’s hotter in cities’ low income areas.

High-Resolution Data Products Help Illuminate Urbanization’s Reach
Two new Landsat-based data products and a mapping tool provide data on man-made impervious surfaces and urban extents throughout the world.


