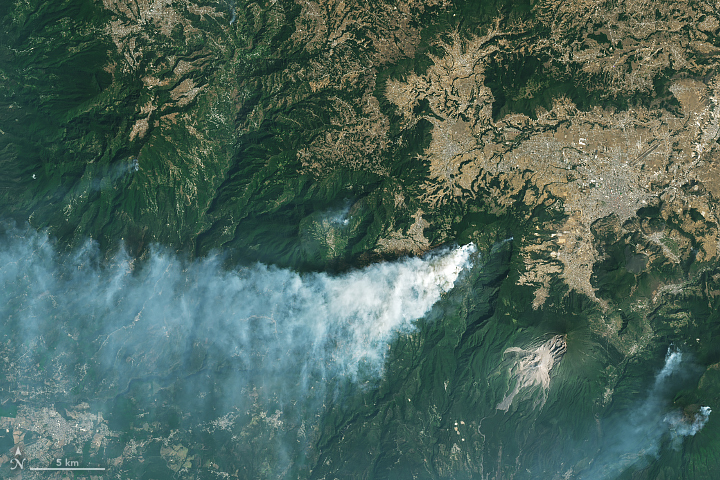
Landsat Next Defined
Landsat Next is on the horizon—the new mission will not only ensure continuity of the longest space-based record of Earth’s land surface, it will fundamentally transform the breadth and depth of actionable information freely available to end users. Take a look at the new capabilities that will define the next Landsat mission.