Presentation title:
Rapid Loss of Lakes on the Mongolian Plateau
What are the major findings of your research?
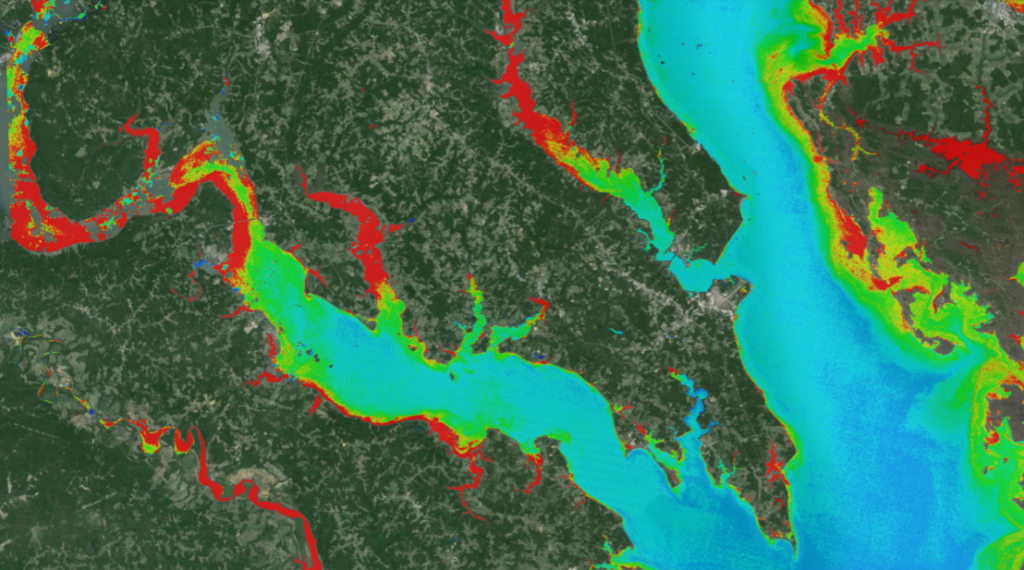
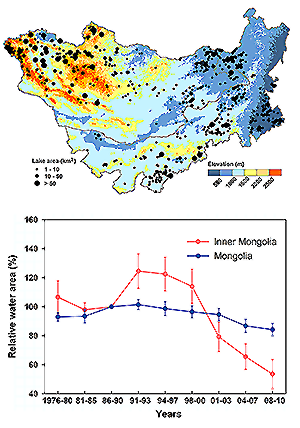
We found a rapid loss of lakes on the Mongolian plateau in the past decades: the number of lakes with a water surface area greater than one square kilometer decreased from 785 in the late 1980s to 577 in 2010, with a greater rate of decrease (34.0%) in Inner Mongolia of China than in Mongolia (17.6%).
This decrease has been particularly pronounced since the late 1990s in Inner Mongolia, and the number of lakes greater than ten square kilometers has declined by 30.0%. The statistical analyses suggested that in Mongolia precipitation was the dominant driver for the lake changes, and in Inner Mongolia coal mining was most important in the region’s grassland area and irrigation was the leading factor in its cultivated area.
What insight did you gain from Landsat that would have been impossible to glean otherwise?
Landsat data is great, with both long-term temporal coverage and fine spatial resolution (30 m)—this is perfect for monitoring lake area changes. Other remotely sensed images fail to provide either fine spatial resolution or long-term temporal coverage.
How can your research help the people suffering most from the rapid loss of lakes on the Mongolian Plateau?
Our research was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, and many media outlets have reported it. The Chinese government is paying attention to the mining issues in Inner Mongolia.
Co-authors:
Jingyun Fang
Peking University
Xia Zhao
IB Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Shuqing Zhao
Peking University
Haihua Shen
IB Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Huifeng Hu
IB Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Zhiyao Tang
Peking University
Zhiheng Wang
Peking University
Qinghua Guo
IB Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Reference:
Tao, Shengli, Jingyun Fang, Xia Zhao, Shuqing Zhao, Haihua Shen, Huifeng Hu, Zhiyao Tang, Zhiheng Wang, and Qinghua Guo. 2015. “Rapid loss of lakes on the Mongolian Plateau.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 112 (7):2281-2286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411748112.
Anyone can freely download Landsat data from the USGS EarthExplorer or LandsatLook.
Further Reading:
+ Landsat at #AGU15