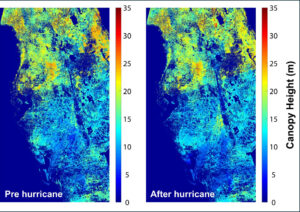
Mapping Forest Damage from Hurricane Milton on Florida’s West Coast
Rising sea levels and increased ocean temperatures are supercharging hurricanes. Using satellite data can help monitor vulnerable ecosystems.

Rising sea levels and increased ocean temperatures are supercharging hurricanes. Using satellite data can help monitor vulnerable ecosystems.
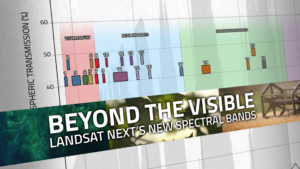
With Landsat Next’s 26 new spectral bands, we’ll be able to see our planet like never before. Landsat Next’s enhanced capabilities will provide scientists, farmers, and decision-makers with critical data to tackle global challenges.

A NASA and U.S. Geological Survey (USGS)-supported research and development team, OpenET, is making it easier for farmers and ranchers to manage their water resources with the FARMS tool.

New research led by Landsat 8/9 Project Scientist Chris Neigh used Landsat and ICESat-2 data to investigate how boreal forests growth could sequester carbon.

Using NASA data, researchers can track vegetation changes around the planet, not just in forests but also in grasslands and savannas like the Brazilian Cerrado.

Between October 2023 and October 2024, the four dams of the Klamath Hydroelectric Project were taken down, opening more than 400 miles of salmon habitat.

Grasslands tend to get left out of conservation discussion. New research from the World Resources Institute maps how they’ve changed over the past 20 years.

Wildfires have been increasing in frequency and size across North America in recent years. British Columbia is no exception to that trend; more than 4% of the heavily-forested province has burned since 2017. In 2023, Canada saw its worst wildfire season in recorded history. These high intensity fires affect ecosystem health and local economies, as timber is a major industry in BC.
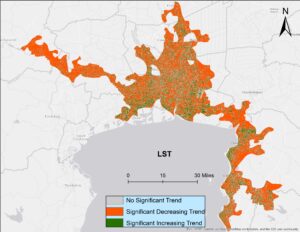
Looking at urban heat islands, researchers found that changing trends in vegetation influence land surface temperature in the Lower Mekong Delta cities.

A cadre of former Landsat Science Team members posit that realizing progress towards global sustainability goals would be substantially aided by 13 essential, regularly-updated global data products made with open-access and freely-available Landsat and Sentinel-2 datasets.
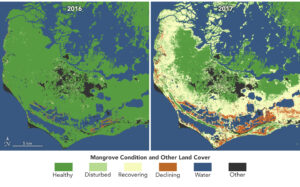
Mangroves, the iconic trees and shrubs of the Florida Everglades, are under increased stress due to more frequent, intense hurricanes.
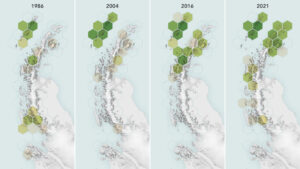
Using observations from Landsat 5 through Landsat 8, scientists determined that the area of vegetated land on the Antarctic Peninsula grew from 0.86 to 11.95 square kilometers (0.33 to 4.61 square miles) between 1986 and 2021.
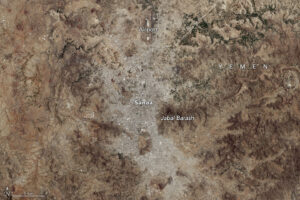
As any urban dweller who has lived through a heat wave knows, a shady tree can make all the difference. But what happens when there’s no shade available?

From his South Dakota roots to leading NASA’s agricultural program, Brad Doorn’s mission has remained the same: help farmers feed the world.
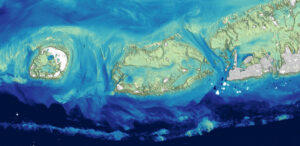
Scientists at the U.S. Geological Survey have developed a new way to measure ocean depth, or bathymetry, in shallow nearshore environments using Landsat data.

Landsat collects data that helps effectively deal with intensifying wildfires—at all stages of the fire cycle.
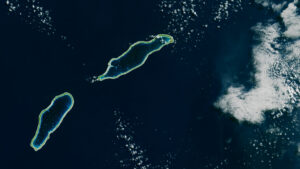
Monitoring the temperature of tiny atoll lagoons is important for the local economy and ecosystem. A new study shows that Landsat can help.

With Landsat-based ET embedded in more and more water rights and conservation tools, Willardson and the Western States Water Council are eager to see Landsat Next with its higher spatial resolution, more frequent observations, and additional spectral bands, built and launched.
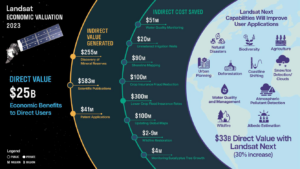
A new report about the Landsat satellite program – a partnership between the U.S. Geological Survey and National Aeronautics and Space Administration – calculates its 2023 value at $25.6 billion—a marked increase from its 2017 estimate of $3.45 billion.

The Amazon is in trouble. Researchers found that, between 2000 and 2022, the Brazilian Amazon lost about 10% of its natural non-forest vegetation.

In a new study, researchers used GPS tracking data and satellite imagery to map elephant movement in northwestern Namibia, looking for corridors of connectivity.

In Taiwan, earthquakes are linked to shallow stores of magma. New research explores this connection by linking land surface temperature with earthquakes.

Warming global climate is changing the vegetation structure of forests in the far north. It’s a trend that will continue at least through the end of this century, according to NASA researchers.

A new study tracks the shifting dynamics of wildfires in western North America. Using Landsat-derived datasets and active fire information from geostationary satellites, researchers found that fires are burning through the night more often—and drought is partially to blame.

A recent national report finds Landsat satellites to be a vital source of data to support U.S. agriculture and forest activities in the United States. The report also supports the continuation of the Landsat Satellite Program as essential to Americans in terms of the value and benefits Landsat delivers every year.
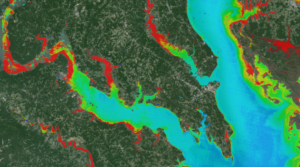
A combination of Landsat and Sentinel-2 imagery, NASA near real-time data, and machine learning provides near real-time access to high-resolution water quality maps.

NASA announced in a contract release that Raytheon Company will build the series of Landsat Next instruments. Landsat Next represents a quantum leap in measurement capabilities with improved temporal, spatial, and spectral resolutions.

In the FY23 Aeronautics and Space Report released on May 23, 2024, a multitude of Federal agencies report work informed by Landsat data.
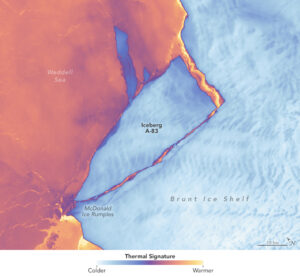
The Brunt Ice Shelf lost a large wedge of floating ice, the third sizeable iceberg to calve from the shelf in recent years. The TIRS instrument on Landsat 9 captured false-color images of the calving.

The Australian company Indji Systems uses a variety of satellite data to provide real-time hazard monitoring and alerts to utility and renewable energy companies across Australia, North America and Europe.

More water is taken from the Colorado River than it has to give. Better water use accounting made possible by Landsat provides needed guidance for difficult water use decisions.
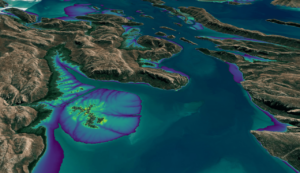
This month, the Digital Earth Australia (DEA) team released a new Landsat and Sentinel-2 based intertidal data product. The new data set characterizes the tidal shoreline zone of Australia in more detail than ever before.

NASA’s Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 (HLS) project is a groundbreaking initiative that combines data from Landsats 8 & 9 with the European Space Agency’s Sentinel-2A & 2B satellites.