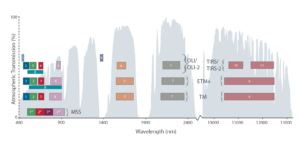
Every full moon, Landsat 8 turns its back on Earth. As the satellite’s orbit takes it to the nighttime side of the planet, Landsat 8 pivots to point at the moon. It scans the distant lunar surface multiple times, then flips back around to continue its task of collecting land-cover information of the sunny side of Earth below. These monthly lunar scans are key to ensuring the land-imaging instrument aboard Landsat 8 is detecting light consistently. For a well-known and stable source of light, nothing on our planet beats the moon, which lacks an atmosphere and has an unchanging surface, barring the odd meteorite.