By Laura E.P. Rocchio
Dr. Kathleen Treseder is a Professor and Vice Chair in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at the University of California Irvine. Today at #AGU16, she gave a talk describing how fire severity affects soil microbes. Here’s what Dr. Treseder shared with us about her research:
Presentation Title
Fire Severity Influences the Response of Soil Microbes to a Boreal Forest Fire
What are the major findings of this research?
We found that soil microbes in a boreal forest were sensitive to fire severity. The more severe the fire, the stronger the decline in microbial biomass. In turn, microbial production of CO2, a greenhouse gas, was inhibited more after severe fires. In addition, mycorrhizal fungi, which improve the growth of forest trees by providing nutrients, were particularly harmed by severe fires.
What are the implications of your findings?
Severe fires are expected to become more common under climate warming, especially in northern ecosystems like boreal forests. We found that this trend could alter how microbes function in the soil, with potential consequences for atmospheric CO2. Severe fires seem to partially sterilize soils, removing microbes. As a result, soil function changes. It appears that decomposition by microbes declines, so less CO2 is released to the atmosphere. This may slow the progression of global warming to some extent. At the same time, mycorrhizal fungi are lost from the soil. Since many boreal forest trees rely on mycorrhizal fungi, their loss might slow the recovery of the forests.
What insight did you gain from Landsat that would have been impossible to glean otherwise?
We used Landsat data to quantify fire severity in a large fire scar. Most of this scar was otherwise inaccessible, so there was no other way to characterize the fire severity across this landscape. Because we could assess variation in fire severity across the scar, we could then scale-up our results from our smaller plot-based measurements.
How would you describe the importance of microbial biomass and fungal communities to the health of boreal forest ecosystems?
Microbes are critical components of boreal forests, since they decompose dead material, produce CO2, and improve tree growth. Without decomposer microbes, the boreal forest would be dominated by dead plant litter. Without mycorrhizal fungi, signature trees like black spruce, white spruce, and aspen would be stunted or absent.
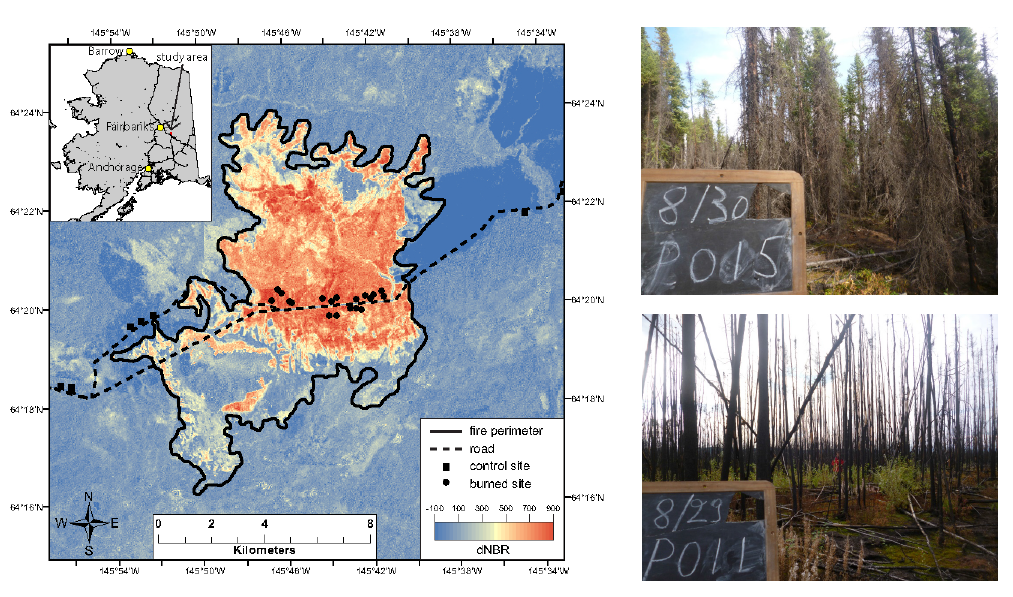
Co-authors:
Sandra R Holden
University of California Irvine
Brendan M Rogers
Woods Hole Research Center
James Tremper Randerson
University of California Irvine
This research was made possible by a NASA Carbon in Arctic Reservoirs Vulnerability Experiment (CARVE) grant awarded to James Randerson.
Anyone can freely download Landsat data from the USGS EarthExplorer or LandsatLook.
Further Reading:
+ Landsat Abounds at #AGU16






