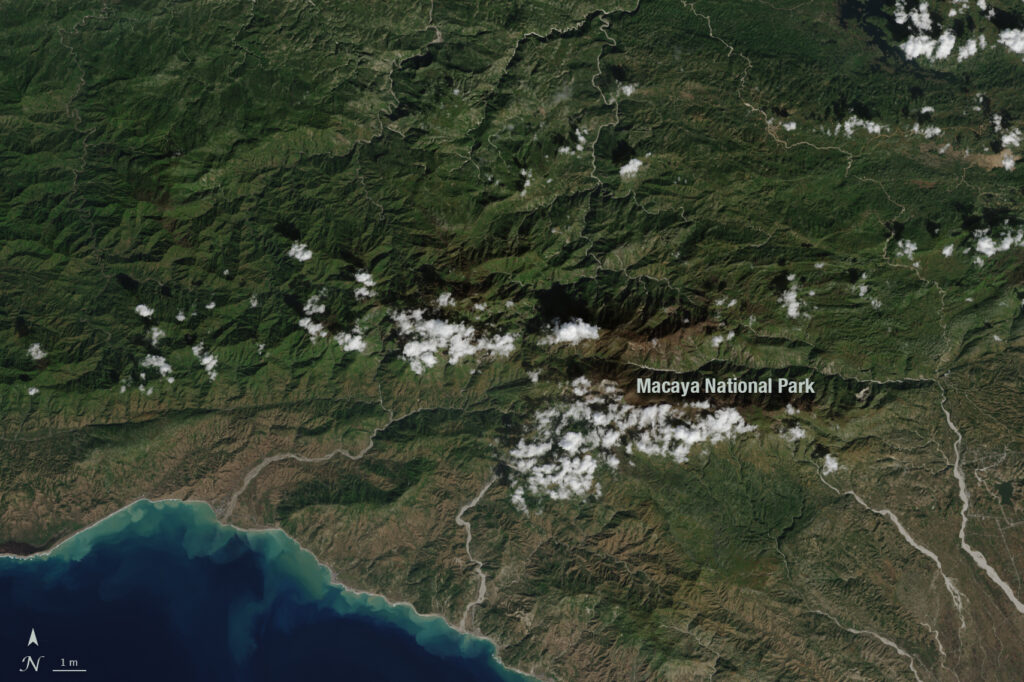
By Laura E.P. Rocchio
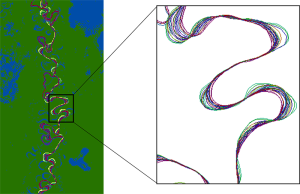
Joshua Ahmed from Cardiff University studies how river meanders evolve. Using Landsat data to examine river movement through time, his team has made new observations about river channel change. He presented his findings at #AGU15.
Presentation title:
Sediment driven meander migration in the Amazon Basin
What are the major findings of your research?
Our research suggests that the way in which meanders evolve through time can dictate how quickly a river increases its sinuosity. If a bend grows predominantly in the downstream direction, it lengthens more quickly. We also show that this bend growth behaviour may be attributed to the sediment load carried by the reach.
What insight did you gain from Landsat that would have been impossible to glean otherwise?
Landsat enabled us to collect a multi-decadal record of the reaches at almost annual resolution. By extending our record into the past we were able to examine how the reaches changed through time providing us with a truly invaluable dataset.
Will your findings advance the state of knowledge about meander migration?
Yes, we believe our results will help to shed some light on the drivers of channel change and help us understand how river channels may respond to externally controlled factors, like sediment load. This can have implications for channel evolution models, riparian habitat development and the safety of floodplain infrastructure.
Co-authors:
Jose Constantine
Cardiff University
Thomas Dunne
University of California Santa Barbara
Anyone can freely download Landsat data from the USGS EarthExplorer or LandsatLook.
Further Reading:
+ Rivers through time, as seen in Landsat images, Hindered Settling Blog
+ Landsat at #AGU15







