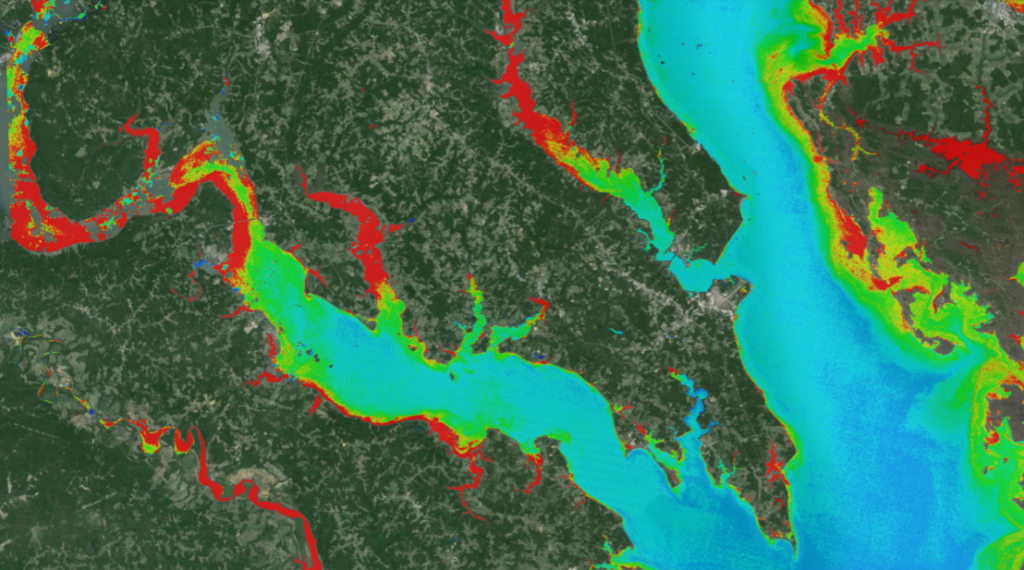
Landsat imagery provides critical vegetation and fuels information that is used to model fire behavior and make tactical decisions. After a fire, scientist and land managers use Landsat imagery to determine the severity of the fire’s effect and to monitor the recovery of the land.
Both images are false-colored to allow identification of critical vegetation and fuels information. In the images fire appears bright red, vegetation is green, smoke is blue, clouds are white, and bare ground is tan-colored.
The USGS supports both the Department of the Interior and U.S. Forest Service wildfire response. Throughout the fire season, USGS regularly uploads images for wildfires from several satellites to the Hazard Data Distribution System. These remotely sensed data are used by wildfire responders to map potential risks to communities and determine immediate post-fire effects. So far in 2013, 2,156 images have been distributed for wildfires.
The USGS helps staff the Geospatial Multi-Agency Coordination Group (GeoMAC). The GeoMAC viewer is a mapping application that allows fire managers and the public to access online maps of current fire locations and fire perimeters. Currently, for 2013, GeoMAC is maintaining up-to-date perimeter information for 620 wildfires across the United States.
Landsat is a joint effort of both USGS and NASA. Landsat images are unique in that they provide complete global coverage, they are available for free, and they span more than 41 years of continuous earth observation.
Source: Jon Campbell, U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey
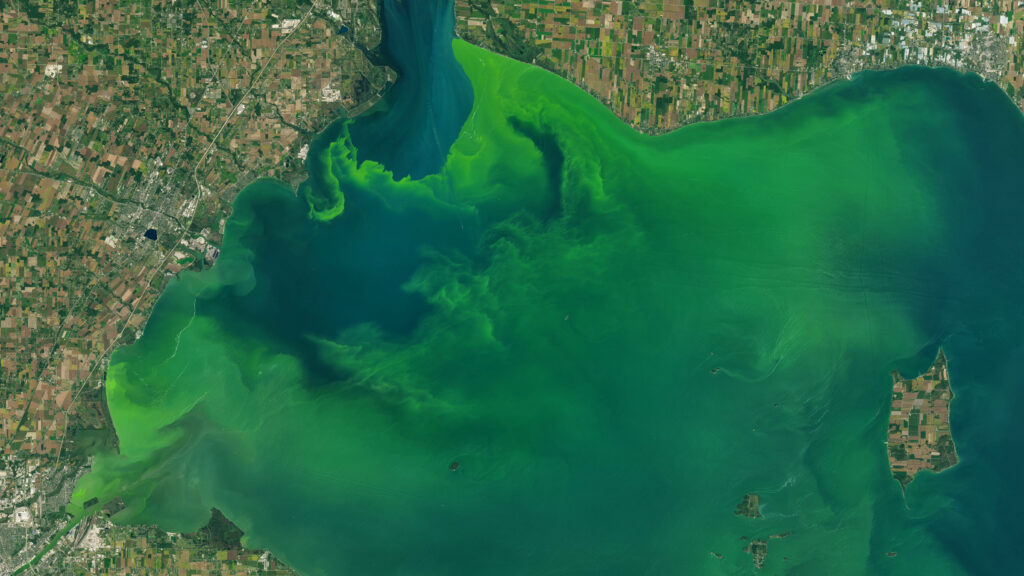

Be Part of What’s Next: Emerging Applications of Landsat at AGU24
Anyone making innovative use of Landsat data to meet societal needs today and during coming decades is encouraged to submit and abstract for the upcoming “Emerging Science Applications of Landsat” session at AGU24.