By Laura E.P. Rocchio
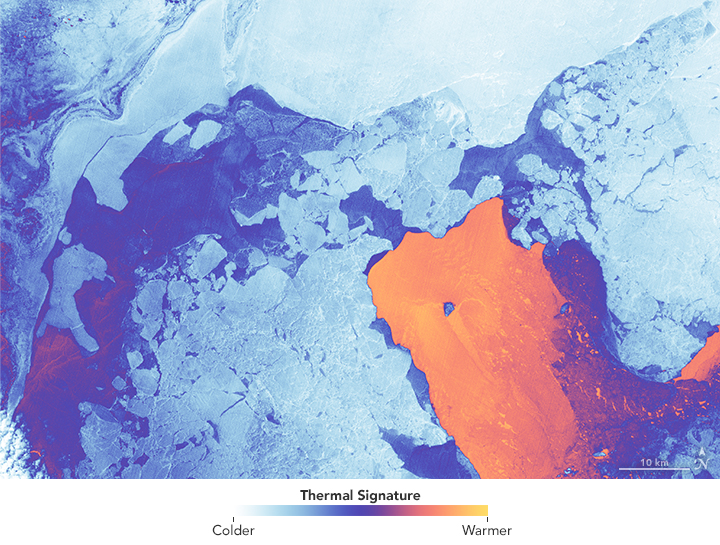
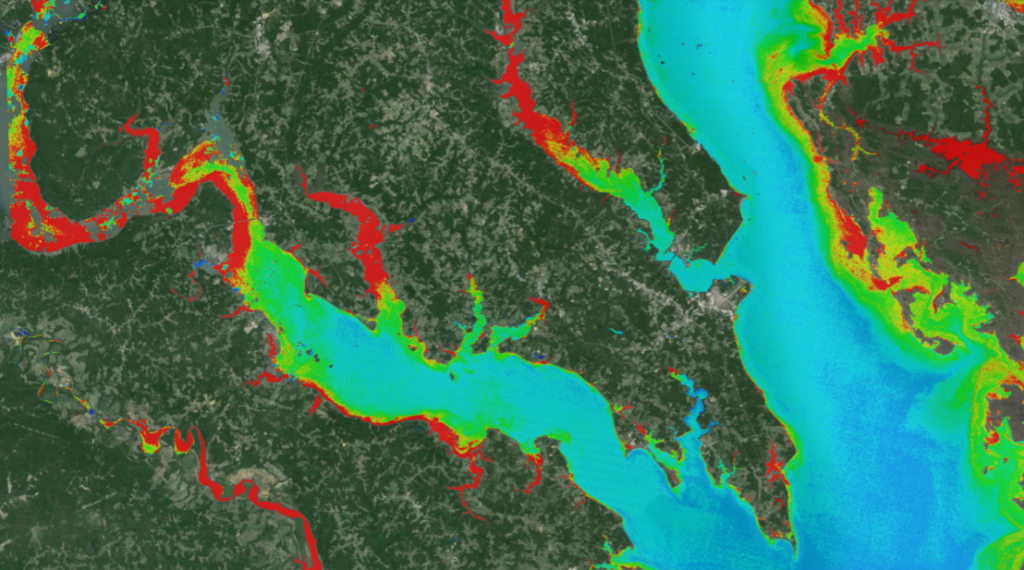
This past February we celebrated the 10-year launch anniversary of Landsat 8. For a decade, Landsat 8 with its two scientific instruments—the Operational Land Imager (OLI) and the Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS)—has collected data about Earth’s surface. Providing information that is used routinely for environmental resource management around the world. The thermal information measured by TIRS has been particularly crucial for water management.
Yet, Landsat 8’s initial design, unlike that of preceding Landsats (4, 5 ,7), did not include a thermal instrument. Early return on investment sentiment was that the thermal data user group was small, and their applications didn’t warrant the additional cost of thermal data collection.
A faction of water managers in the U.S. West was determined to set the record straight, correct that misperception, and get a thermal sensor onto Landsat 8.
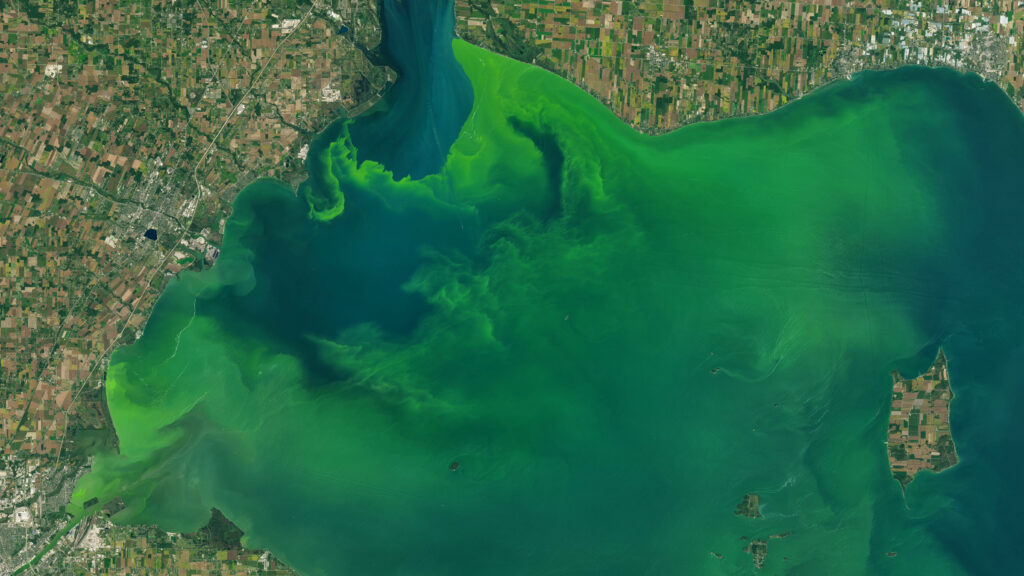
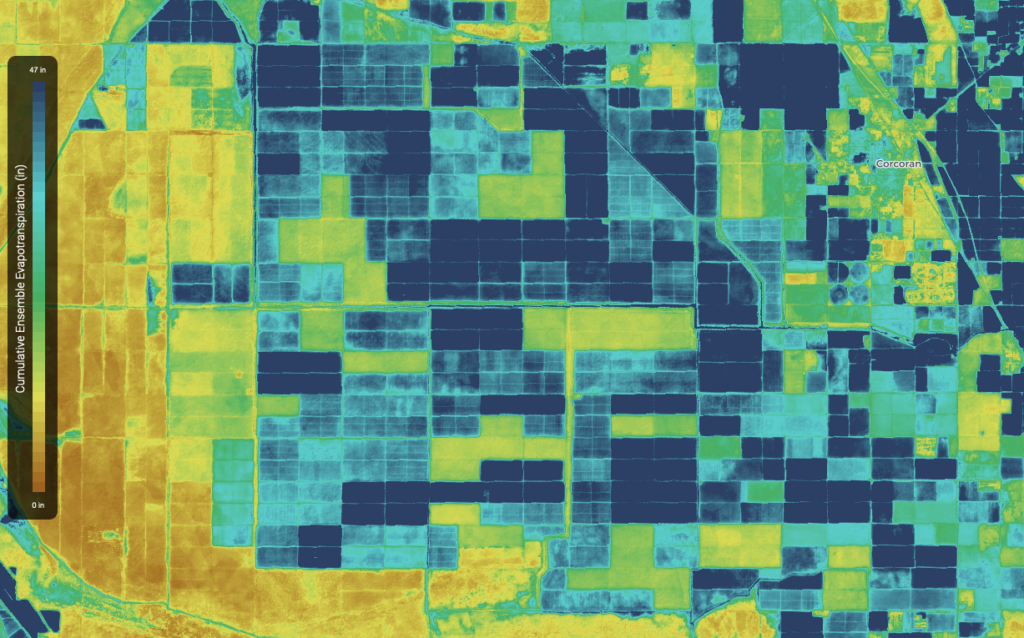
The Idaho Department of Water Resources had started using Landsat thermal data (together with its near infrared and shortwave infrared data) to map water consumption in 2000. Their water planners soon came to rely on Landsat-derived evapotranspiration (ET) data for long-term water supply estimates and water demand analysis. They increasingly found themselves turning to Landsat ET data to provide information for water rights legal proceedings. By 2007, twelve western states were actively using Landsat thermal data in their water management operations.
With the very real prospect of Landsat 8 launching without a thermal sensor and water managers losing their only data source for field-level water consumption measurements, western water managers began a sustained letter-writing campaign that changed the course of history. Governors, senators, state engineers, and natural resource department directors worked together to let Congressional decision-makers know that Landsat thermal data provided the “only efficient and accurate way to map how much and where water is being consumed.” Congress was made aware that continuing to have thermal sensors on Landsat satellites was fundamental for meeting the challenge of western water supply. The message had impact.
By 2009, funds were secured to add a thermal sensor to Landsat 8—the same year that Idaho won Harvard’s prestigious Ash Institute Innovations in American Government Award for its Landsat-based water management tool.
Challenge After Challenge: Getting TIRS Built
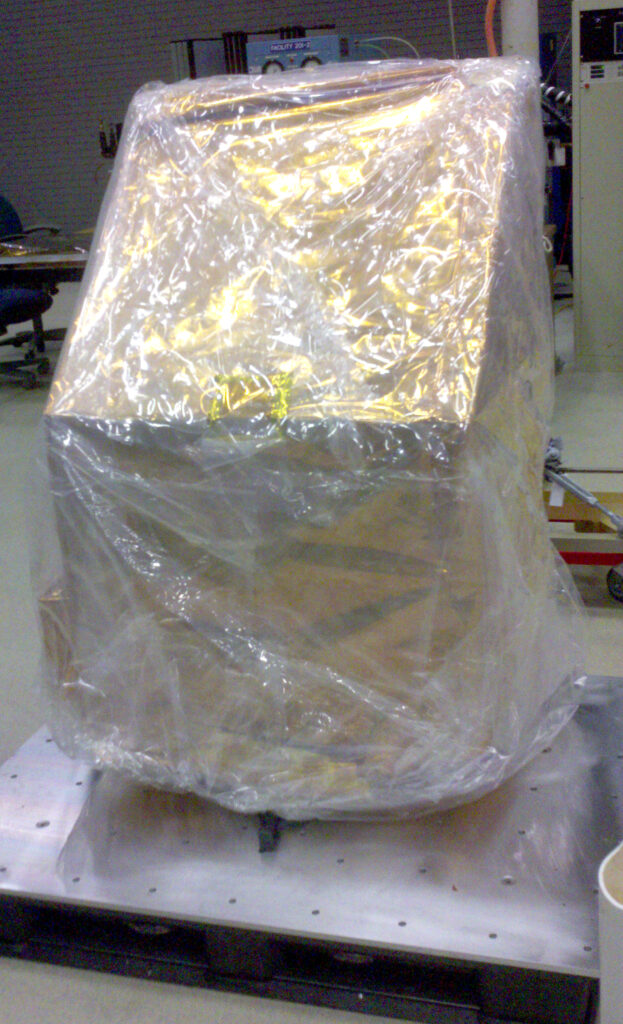

It was late in the game when funding for TIRS came through, and the thermal sensor had to be built quickly. Given the tight timeline, NASA decided to build TIRS as a “Class C” instrument, a system with less redundancy, required to satisfy only a three-year design life.
TIRS was built in-house at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It was a fast build. The pressure was high. With an extremely demanding schedule to meet, the threat of cancelation was relentless. NASA created a mass model—a piece of metal that weighed the same amount as the TIRS instrument—that would fly as “dead weight” if TIRS wasn’t ready in time.
But the design team came through; TIRS flew on Landsat 8.
TIRS—the sensor that very nearly wasn’t—has now been imaging Earth for a decade.
“I’m very glad that TIRS has lasted this long on-orbit,” says Landsat calibration scientist Matthew Montanaro. “That’s a testament to the hard work put in by the TIRS team during development, and the Cal/Val and Flight Operations teams that continue to monitor it on-orbit and step in to fix any issues that arise.”
Thanks to TIRS, satellite-based water management has continued, and projects like OpenET—“filling the biggest data gap in water management”—have been made possible.
The value of medium-resolution thermal data has been cemented.
“I highly doubt there will ever be a Landsat mission without a thermal band going forward,” Montanaro speculates.
Related Reading & References
Idaho Department of Water Resources, “Landsat Thermal Band: Importance of Landsat for Water Resources in Idaho.” Accessed May 30, 2023.
Goward, Samuel N., Darrel L. Williams, Terry Arvidson, Laura E.P. Rocchio, James R. Irons, Carol A. Russell, and Shaida S. Johnston. 2017. Landsat’s Enduring Legacy: Pioneering Global Land Observations from Space. Bethesda, MD: American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing; pp. 361-362.
Landsat 8 Thermal Data Ghost-Free After Stray Light Exorcism; Landsat Science