By Sofie Bates, NASA’s Earth Science News Team

April 20, 2021 • Fertilizers used in farming contain high amounts of nutrients, such as phosphorous, to help crops grow. But these same nutrients can cause unwanted plant growth and potentially harm ecosystems miles away if agricultural runoff flows into nearby rivers, lakes, or coastal waters.
These effects represent one of the many ways that the different parts of the Earth system are connected. Waterways like rivers and streams are natural highways that connect areas hundreds to thousands of miles apart. They are also essential ecosystems for fish and other aquatic life, as well as sources of drinking water and recreational areas for people. Earth-observing satellites from NASA and its partners have a unique perspective from which to study the links between water and other parts of the Earth system – and are uniquely poised to help researchers address the consequences of those links, namely water quality.
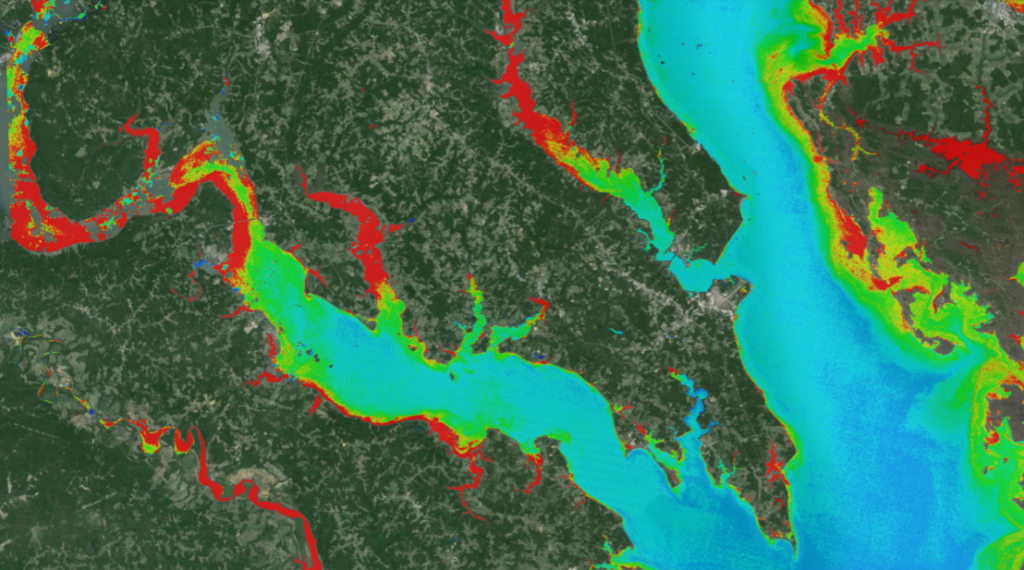
Most bodies of water contain microscopic, photosynthesizing organisms called cyanobacteria, which are harmless at normal levels. Individual cyanobacteria are tiny, visible only under a microscope. But certain conditions – lots of sunlight, stagnant water, and high amounts of nutrients like those in fertilizers – allow cyanobacteria populations to grow exponentially. The result is scummy green water that can be seen from space. These events, called harmful algal blooms, can lead to economic losses and poor water quality, and pose a health risk to humans and animals.
Green Lakes and Satellites
Cyanobacteria have a photosynthesizing pigment called chlorophyll-a, which gives algal blooms a green hue when seen from space. Satellites can measure the concentration of chlorophyll-a in a body of water, allowing scientists to estimate the amount of cyanobacteria in the water. Several Earth-observing satellites are used to monitor algal blooms from space: NASA’s Terra and Aqua satellites, the joint NASA/USGS Landsat satellites, and the European Space Agency’s Copernicus Sentinel-2 and Copernicus Sentinel-3 satellites. Which one is used often depends on the resolution of the satellite instrument and which satellite passes over the algal bloom at the right time to capture a cloud-free image.
Harmful algal blooms are often hard to predict. NASA is part of a multi-agency Cyanobacteria Assesment Network (CyAN project), which includes the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), to monitor harmful algal blooms and other water quality issues. In 2021, NASA will launch Landsat 9, gaining another Earth-observing satellite to help track algal blooms from space.
The Cost of Harmful Algal Blooms
During an algal bloom, the water becomes covered with clumpy green scum that gives off a musty smell. Aquatic recreation like swimming and water sports are often suspended until the levels of cyanobacteria return to safe levels. Harmful algal blooms also lead to economic losses in a less obvious sector: healthcare.
A NASA-funded study found that detecting harmful algal blooms early led to significant savings on healthcare, lost work hours and other economic losses totaling approximately $370,000. The study, published in the journal GeoHealth, focused on a 2017 algal bloom in Utah Lake. The team compared the economic losses from two scenarios: the real-world scenario in which satellites detected the bloom, and a hypothetical scenario in which the decision was based on human observers and on-site testing.
Satellite data showed the beginnings of an algal bloom in time for Utah public health officials to put up warning posters by June 29, 2017 to alert visitors to use caution while boating, not to swim or water ski, and how to fish safely. In the hypothetical scenario, scientists calculated what would’ve happened if officials waited for human observers to report the bloom and confirm with on-site testing, then posted signs on July 6. The week-long delay would have cost $370,000 according to health economics models, showing how detecting harmful algal blooms early can result in significant savings on healthcare and other economic costs.
Harmful algal blooms pose a health risk to fish and other wildlife as well as humans. During an algal bloom, cyanobacteria grow exponentially. That algae uses up oxygen in the water as it decomposes, which decreases the amount of oxygen dissolved in the water and can asphyxiate fish and other aquatic animals. The most severe cases lead to massive fish die offs. In 2016, some lagoons in Florida became obscured by the upturned white bellies of thousands of dead fish after an algal bloom.
Instances like these are a reminder that ecosystems on Earth are interconnected, and actions in one part of the planet have downstream impacts on other ecosystems and humans.