
Meet Dr. David Lagomasino
Coastal ecosystems are some of Earth’s most biologically diverse environments, especially coastal mangrove forests. Dr. Lagomasino uses Earth observing data to study these vital biomes.

Coastal ecosystems are some of Earth’s most biologically diverse environments, especially coastal mangrove forests. Dr. Lagomasino uses Earth observing data to study these vital biomes.

Study of two metro areas finds where parks, trees and other green spaces are located.

NASA has funded four projects to create new, virtual portals to share a wealth of biodiversity information with land stewards around the world.

Dr. Eric Bullock uses Earth observation data to explore the consequences of land use and land cover change in high biodiversity areas.

Invasive species cost the U.S. economy approximately $120 billion a year and disrupt the dynamics of ecosystems. Researchers are increasingly using remote sensing to map where invasive species are and where they could spread in order to minimize their damage.

Landsat data (since 1972) is helping scientists Sean Healey and Zhiqiang Yang of the Rocky Mountain Research Station (U.S. Forest Service) study the long-term impact of the May 18, 1980, eruption of Mount St. Helens.
The first NASA/USGS Landsat satellite was launched just two years after the first Earth Day and successive Landsat satellites have been helping us understand our planet ever since.

The 2020 Earth Science Week poster was created as a joint effort between NASA, AmericaView, and USGS and incorporates Landsat imagery to engage with and communicate to the public this year’s American Geological Institute (AGI) theme: “Earth Materials in Our Lives”.

USDA researcher Martha Anderson uses satellites and instruments like Landsat and ECOSTRESS to see how stressed plants are from space.

This bird’s-eye view of the relationship between temperature and bird biodiversity will help conservationists figure out where to prioritize their efforts in a warming world.

Researchers and conservationists around the world are using data and images from NASA satellite instruments to manage and track living creatures of all kinds.

Grape growers like Gallo are using data from Earth-observing satellites to better track soil and vine moisture levels, understand vine water use and plan grapevine irrigation.

Landsat 9 has successfully passed its Mission Operations Review.
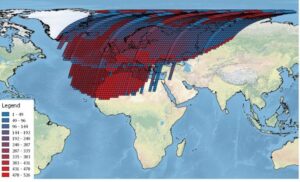
ESA has processed its historical collection of Landsat MSS data (collected by ESA ground stations) so that it can be easily compared to later Landsat data sets and Sentinel-2 data.

A new satellite-driven biophysical model can make accurate forecasts of crop water use that are critical for farmland water management and sustainability.

Kelp forest cover near Tierra del Fuego appeared to follow approximately four-year cycles that mirror sea surface temperature and El Niño-Southern Oscillation rainfall patterns.

How the fields of epidemiology and remote sensing intersect to help the public.

Landsat imagery shows that bull kelp canopy area can vary dramatically from year to year, and that long-term population trends vary from reef to reef.

Considered one of the world’s richest and most endangered forests, the Atlantic rainforest occupies 15% of Brazil’s landmass in an area that is home to 72% of the population.

The extent of wintertime river ice has declined by 2.5 percentage points globally over the past three decades.

Intertidal wetlands significantly contribute to China’s environmental and ecological diversity, but are facing unprecedented pressures from anthropogenic development, as well as the threat of future sea level rise.

Researchers used Landsat satellites to track changes in surface water temperature for the Sekong, Sesan and Srepok rivers. Within one year of the opening of a major dam, downstream river temperatures during the dry season dropped by up to 3.6ºF.

With Landsat data, farmers can find new ways to grow more crops with less water.
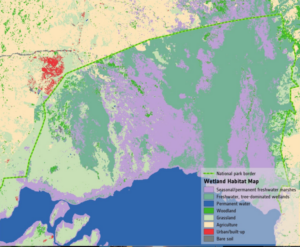
Wetlands worldwide are vanishing at an alarming rate. New satellite-informed maps produced by ESA’s GlobWetland Africa project show how satellite observations can be used for the effective use and management of wetlands in Africa.
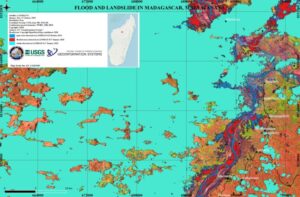
Landsat continues to support the International Disaster Charter.

Plant life is expanding in the area around Mount Everest, and across the Himalayan region, new research shows.

Landsat 9’s two science instruments are now attached to the spacecraft.

Ecologists are using Landsat to locate waterbird habitat that may be vulnerable in dry years.

Landsat-based urban extent and phenology indicators provide new information about urban environments.

Landsat helps monitor changes in artisanal gold mining areas, enabling land managers to prevent and remedy environmental impacts.

There is a dance between the vegetation that thrives along a river’s edge and the availability of water; with Landsat, that relationship is now being understood in ways not previously possible.
IndigoAg is using HLS data to help fulfill its mission of making farms more profitable and sustainable.

Fires in forested watersheds that support drinking water supplies can introduce contaminants that overwhelm current treatment capabilities. Earth observation data are helping.