
Mapping Twenty Years Of Historical US Midwestern Corn And Soybean Information with Landsat
A new data set uses Landsat data to extend the Crop Data Layer back in time.

A new data set uses Landsat data to extend the Crop Data Layer back in time.

A new web-based platform called OpenET will soon be putting satellite data in the hands of farmers, water managers and conservation groups to accelerate improvements and innovations in water management.
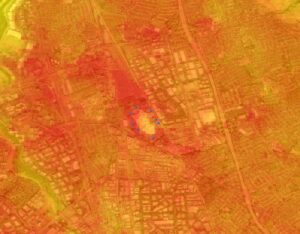
Satellite images are helping to reveal how COVID-19 lockdown measures are impacting food security, urban surface heat, water quality and aquatic ecosystems, and more in NASA-funded studies.

Landsat and ICESat-2 satellite data have made it possible for scientists to develop maps showing the “quality” of tropical forests.
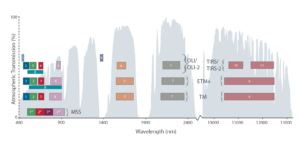
Learn more about the atmospheric transmission data used for our Landsat spectral band comparison graphic.

Using Landsat, researchers have created the first map of the causes of change in global mangrove habitats between 2000 and 2016—a valuable tool to aid conservation efforts for these vital coastline defenders.

In Beck’s “Hyperlife” video, the abstract beauty of our planet morphs from geographic location-to-location with the flow of the etherial track.

We have Virginia Norwood to thank for the design and engineering that made the Landsat program a success and set the path for modern Earth observation.

Goldberg will launch Cloud to Classroom, an innovative project that uses satellite imagery to help K-12 classrooms understand global environmental change through remote sensing.

In August 1975, Jacques Cousteau and his divers helped determine if Landsat could measure the depth of shallow ocean waters.

The use of satellite data by environmental managers tracking harmful algal bloom outbreaks along lakefronts and coasts can result in earlier detections that yield significant savings on healthcare, lost work hours and other economic costs.

The Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations published an audio article about using geospatial data, including Landsat, to monitor would agriculture on soundcloud.

Coastal ecosystems are some of Earth’s most biologically diverse environments, especially coastal mangrove forests. Dr. Lagomasino uses Earth observing data to study these vital biomes.

Study of two metro areas finds where parks, trees and other green spaces are located.

NASA has funded four projects to create new, virtual portals to share a wealth of biodiversity information with land stewards around the world.

Dr. Eric Bullock uses Earth observation data to explore the consequences of land use and land cover change in high biodiversity areas.

Invasive species cost the U.S. economy approximately $120 billion a year and disrupt the dynamics of ecosystems. Researchers are increasingly using remote sensing to map where invasive species are and where they could spread in order to minimize their damage.

Landsat data (since 1972) is helping scientists Sean Healey and Zhiqiang Yang of the Rocky Mountain Research Station (U.S. Forest Service) study the long-term impact of the May 18, 1980, eruption of Mount St. Helens.
The first NASA/USGS Landsat satellite was launched just two years after the first Earth Day and successive Landsat satellites have been helping us understand our planet ever since.

The 2020 Earth Science Week poster was created as a joint effort between NASA, AmericaView, and USGS and incorporates Landsat imagery to engage with and communicate to the public this year’s American Geological Institute (AGI) theme: “Earth Materials in Our Lives”.

USDA researcher Martha Anderson uses satellites and instruments like Landsat and ECOSTRESS to see how stressed plants are from space.

This bird’s-eye view of the relationship between temperature and bird biodiversity will help conservationists figure out where to prioritize their efforts in a warming world.

Researchers and conservationists around the world are using data and images from NASA satellite instruments to manage and track living creatures of all kinds.

Landsat 9 has successfully passed its Mission Operations Review.
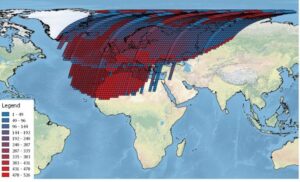
ESA has processed its historical collection of Landsat MSS data (collected by ESA ground stations) so that it can be easily compared to later Landsat data sets and Sentinel-2 data.

A new satellite-driven biophysical model can make accurate forecasts of crop water use that are critical for farmland water management and sustainability.

Kelp forest cover near Tierra del Fuego appeared to follow approximately four-year cycles that mirror sea surface temperature and El Niño-Southern Oscillation rainfall patterns.

How the fields of epidemiology and remote sensing intersect to help the public.

Landsat imagery shows that bull kelp canopy area can vary dramatically from year to year, and that long-term population trends vary from reef to reef.

Considered one of the world’s richest and most endangered forests, the Atlantic rainforest occupies 15% of Brazil’s landmass in an area that is home to 72% of the population.

The extent of wintertime river ice has declined by 2.5 percentage points globally over the past three decades.

Intertidal wetlands significantly contribute to China’s environmental and ecological diversity, but are facing unprecedented pressures from anthropogenic development, as well as the threat of future sea level rise.

Researchers used Landsat satellites to track changes in surface water temperature for the Sekong, Sesan and Srepok rivers. Within one year of the opening of a major dam, downstream river temperatures during the dry season dropped by up to 3.6ºF.