
Bill Kustas: Advancing Water Research Drop by Drop
Kustas’ research informed the new OpenET app that uses Landsat thermal data as a key data input.

Kustas’ research informed the new OpenET app that uses Landsat thermal data as a key data input.

NASA will hold a virtual media briefing at 1:30 p.m. EDT Thursday, Oct. 21, to share a powerful, new, web-based platform to help those who rely on water resources across the drought-stricken western U.S.

For over 30 years, Dr. Beach, aka Dr. Stephen Leatherman, a professor and coast geomorphologist at Florida International University, has created a Top 10 Beach list based on criteria including water and sand quality, safety, and management. You can find his 2021 picks here and see how Landsat views them as well.

In Micronesia, the nation of Palau is building sustainable aquaculture farms in the ocean with the help of satellites.

‘Green tides’ of algae have wreaked havoc across the coastlines of Brittany, France, for half a century due to high levels of agricultural runoff. With efforts to reduce these underway, a new technique using over three decades of satellite images highlights the extent of the continuing problem.
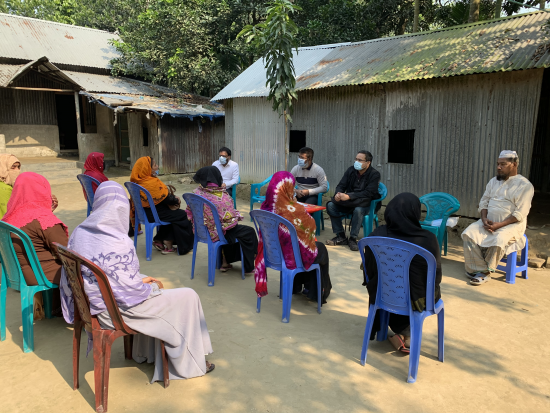

Putting NASA and USGS satellite information at farmers’ fingertips leads to less water use and better crop yields in South Asia.

Harmful algal blooms pose a health risk to fish and other wildlife as well as humans; satellites, including Landsat, are helping public health officials keep people safe.

Landsat helps water resource managers know where to look for dangerous algal blooms in Utah lakes.

Most of Northern California’s kelp forest ecosystem is gone, replaced by widespread ‘urchin barrens’ that may persist long into the future, according to a new study.

Lidar measurements of surface water level combined with Landsat-based surface water maps have enabled the first quantification of how humans impact the water cycle.

Vegetation cover along the Kuiseb River in the Namib Desert has increased over the last 35 years, Landsat has helped show.

The SERVIR team has developed models for groundwater demand based on Earth observations for parameters like rainfall and surface water from satellite missions.

Australia’s natural resource regulator uses drones and satellite imagery to monitor water use and compliance with their water laws across New South Wales to ensure our water resources are protected for generations to come.

Using Landsat to keep an eye on the trees offers an effective way to monitor groundwater along river corridors in the Southwest.

The NASA-funded Navajo Nation Drought Project has built a cloud-based web application that uses Landsat and Sentinel-2 data, among others, to improve drought reporting and management in the Navajo Nation.

Landsat shows some of the ways in which COVID-19 is changing the environment.

Scientist and Landsat data user Africa Flores recently talked with Science Friday about her work.

Scientists are combining data from water samples containing fish DNA with satellite data to find native fish and identify their habitats.
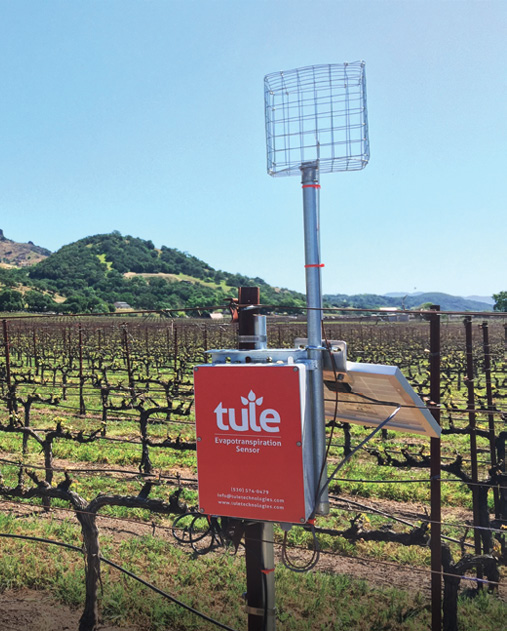

A young start-up is using satellite data to give California farmers better information about water, which can translate into water savings or bigger yield for the same input.
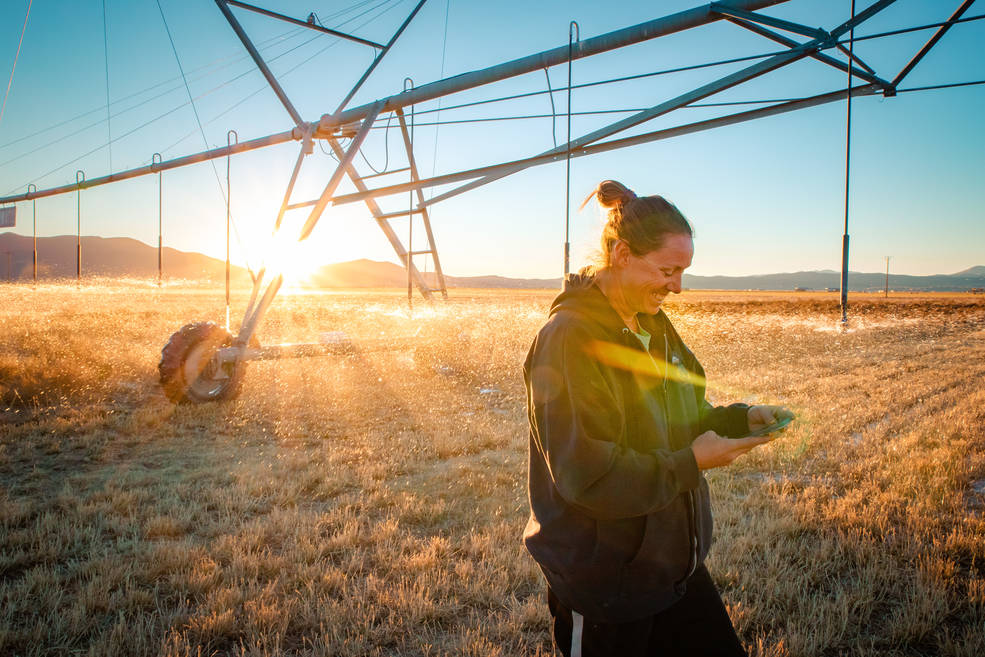

A new web-based platform called OpenET will soon be putting satellite data in the hands of farmers, water managers and conservation groups to accelerate improvements and innovations in water management.
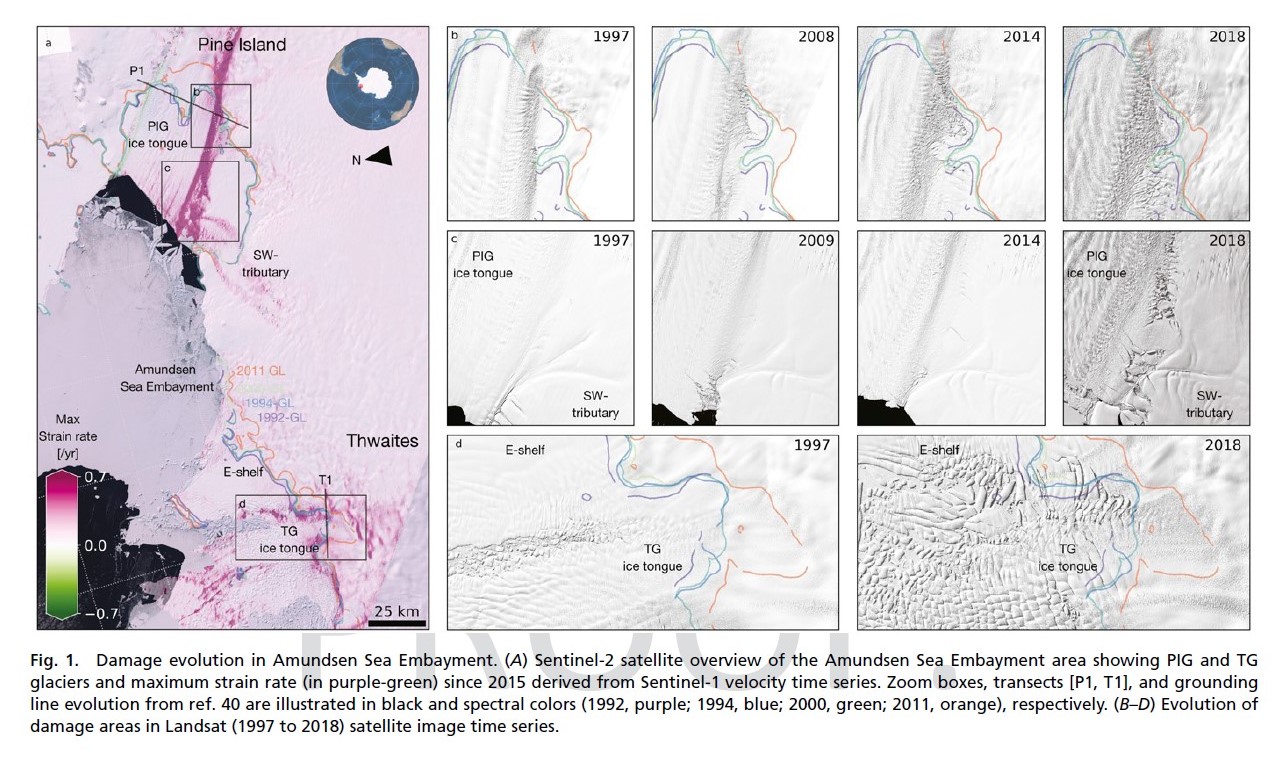
Combined satellite imagery have afforded researchers a new, accurate picture of the rapid development of damage in the shear zones on the ice shelves of Pine Island and Thwaites.

Using 30 years of Landsat data, researchers have found that the volume of glacial lakes worldwide has increased by about 50% since 1990.
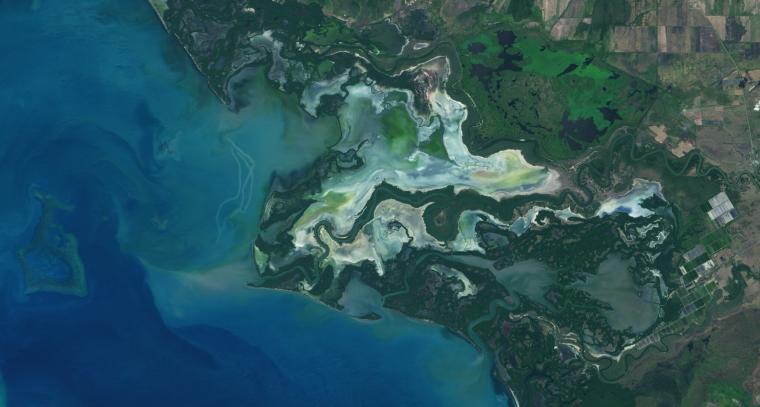

Using Landsat, researchers have created the first map of the causes of change in global mangrove habitats between 2000 and 2016—a valuable tool to aid conservation efforts for these vital coastline defenders.

Goldberg will launch Cloud to Classroom, an innovative project that uses satellite imagery to help K-12 classrooms understand global environmental change through remote sensing.
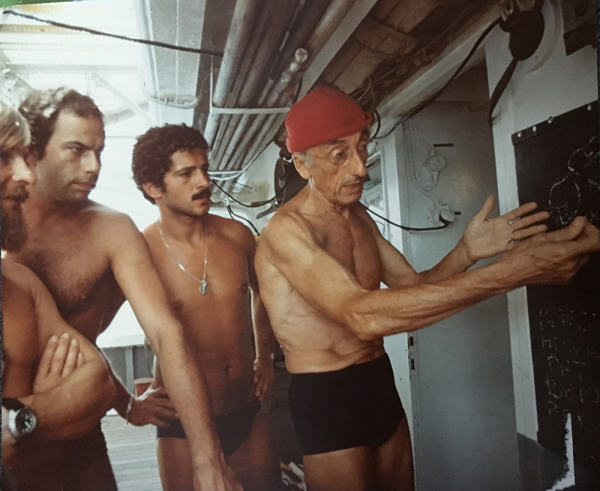

In August 1975, Jacques Cousteau and his divers helped determine if Landsat could measure the depth of shallow ocean waters.

The use of satellite data by environmental managers tracking harmful algal bloom outbreaks along lakefronts and coasts can result in earlier detections that yield significant savings on healthcare, lost work hours and other economic costs.
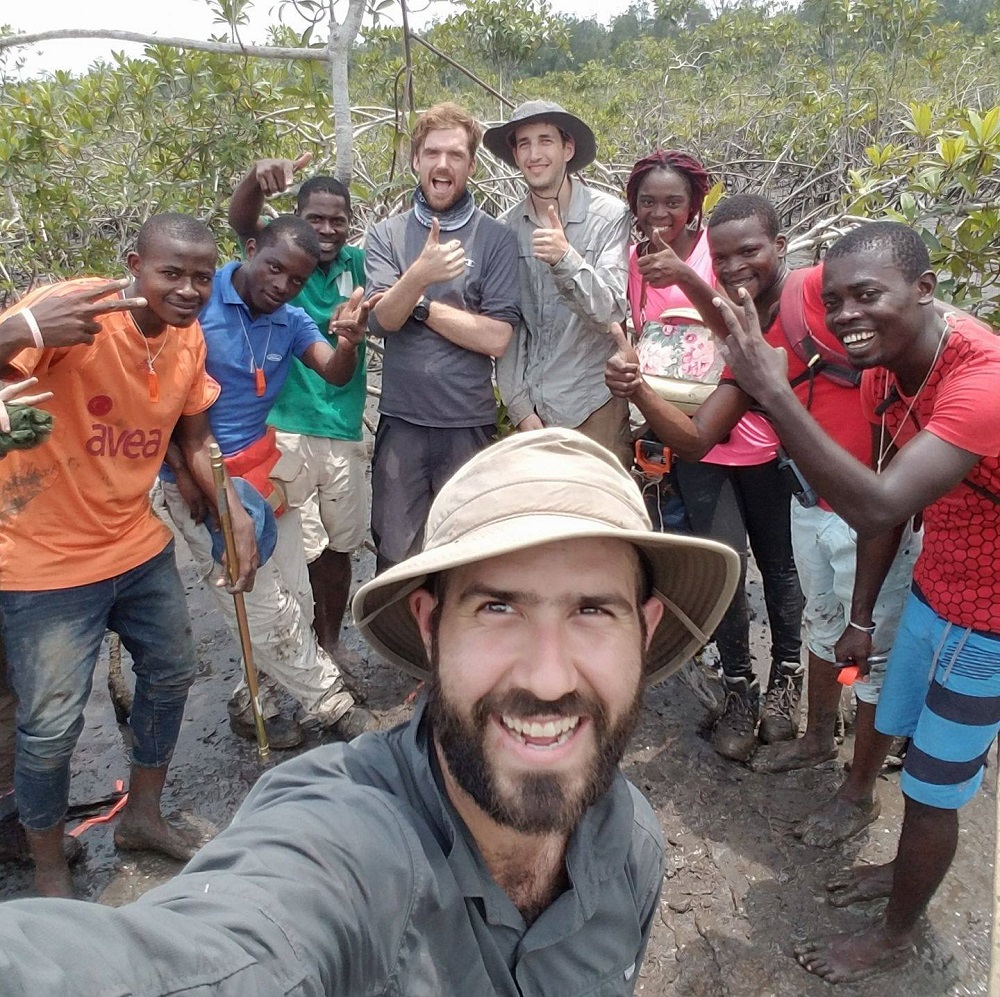

Coastal ecosystems are some of Earth’s most biologically diverse environments, especially coastal mangrove forests. Dr. Lagomasino uses Earth observing data to study these vital biomes.

USDA researcher Martha Anderson uses satellites and instruments like Landsat and ECOSTRESS to see how stressed plants are from space.
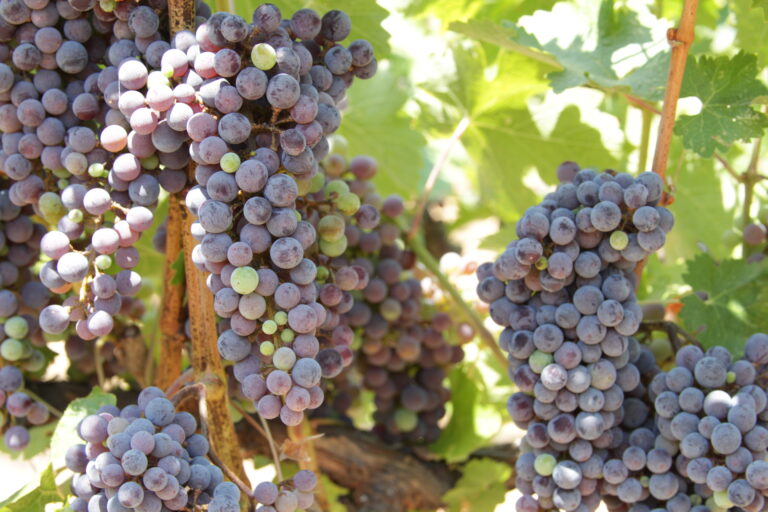

Grape growers like Gallo are using data from Earth-observing satellites to better track soil and vine moisture levels, understand vine water use and plan grapevine irrigation.

A new satellite-driven biophysical model can make accurate forecasts of crop water use that are critical for farmland water management and sustainability.

Landsat imagery shows that bull kelp canopy area can vary dramatically from year to year, and that long-term population trends vary from reef to reef.
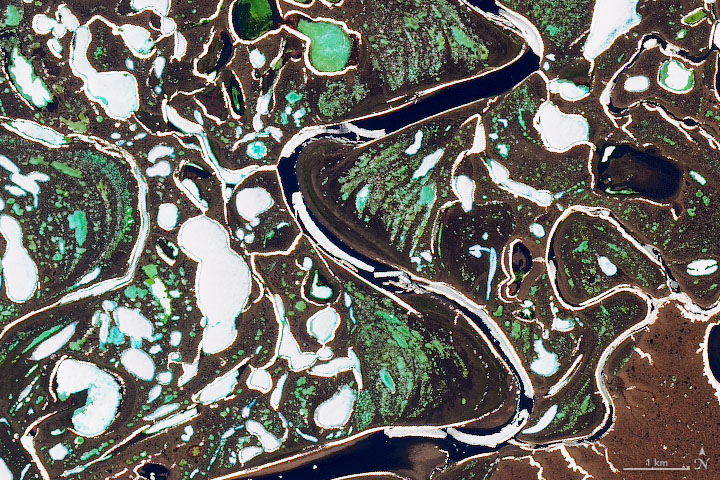
The extent of wintertime river ice has declined by 2.5 percentage points globally over the past three decades.

Intertidal wetlands significantly contribute to China’s environmental and ecological diversity, but are facing unprecedented pressures from anthropogenic development, as well as the threat of future sea level rise.